Health
First babies born in Britain using DNA from 3 people
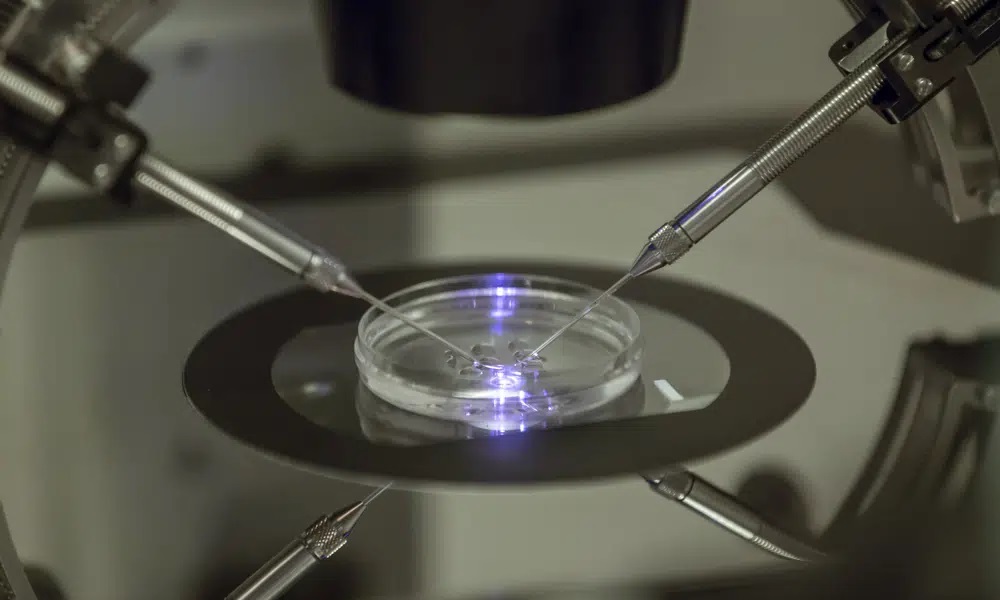

Britain’s fertility regulator on Wednesday confirmed the births of the U.K.’s first babies created using an experimental technique combining DNA from three people, an effort to prevent the children from inheriting rare genetic diseases.
Britain’s Human Fertilization and Embryology Authority said fewer than five babies have been born this way in the U.K. but did not provide further details to protect the families’ identities, Associated Press reported. The news was first reported by the Guardian newspaper.
In 2015, the U.K. became the world’s first country to adopt legislation specifically regulating methods to help prevent women with faulty mitochondria — the energy source in a cell — from passing defects on to their babies.
The genetic defects can result in diseases such as muscular dystrophy, epilepsy, heart problems and intellectual disabilities. About one in 200 children in Britain is born with a mitochondrial disorder. To date, 32 patients have been authorized to receive such treatment.
For a woman with faulty mitochondria, scientists take genetic material from her egg or embryo, which is then transferred into a donor egg or embryo that still has healthy mitochondria but had the rest of its key DNA removed.
The fertilized embryo is then transferred into the womb of the mother. The genetic material from the donated egg comprises less than 1% of the child created from this technique.
“Mitochondrial donation treatment offers families with severe inherited mitochondrial illness the possibility of a healthy child,” the U.K. fertility regulator said in a statement Wednesday. The agency said it was still “early days” but it hoped the scientists involved, at Newcastle University, would soon publish details of the treatment.
Britain requires every woman undergoing the treatment to receive approval from the Human Fertilization and Embryology Authority. The regulator says that to be eligible, families must have no other available options for avoiding passing on genetic disease.
Many critics oppose the artificial reproduction techniques, arguing there are other ways for people to avoid passing on diseases to their children, such as egg donation or screening tests, and that the experimental methods have not yet been proven safe.
Others warn that tweaking the genetic code this way could be a slippery slope that eventually leads to designer babies for parents who not only want to avoid inherited diseases but to have taller, stronger, smarter or better-looking children.
Health
Azerbaijan urged to help improve capacity of Afghan health workers
Acting Minister of Public Health Qalandar Ebad, in a meeting with Azerbaijan’s ambassador, Ilham Mohammadov, called for the country’s assistance in improving the capacity of Afghanistan’s health workers.
The two sides also discussed cooperation in the health sector, capacity building of Afghan health workers, and Azerbaijan’s role in the health sector and other issues, according to a statement released by the Public Health Ministry.
Azerbaijan’s envoy said that his country seeks to cooperate with Afghanistan in a sustainable manner in the field of health.
In other news, the foundation stone for the construction of oxygen production facility was laid at the Indira Gandhi children hospital in Kabul.
Officials of the Ministry of Public Health said that the facility will be built with the financial and technical assistance of the World Health Organization, and with the capacity to produce 200 cylinders of oxygen daily to meet not only the needs of the hospital, but also other health facilities.
Health
Balkh health officials report sharp increase in number of cancer patients
Balkh Public Health Department officials say there has been a significant increase in the number of patients with cancer in the province.
“In 1401, about 2,613 OPD (out patient department) cases were registered with us. In 1402, these figures were 4,912 cases,” said Ehsanullah Kaliwal, the head of the oncology department at Balkh Regional Hospital.
Some doctors say genetic factors, environmental pollution, arbitrary use of medicines, and excessive consumption of meat were reasons for the sharp increase.
One doctor said cancer was also hereditry.
However, a large percentage of cancer patients in Balkh have stomach cancer. Many of them have appealed for the government to improve treatment facilities.
According to health officials, in the first month of this solar year (April), 423 cancer patients visited this hospital for treatment.
Health
Majority of Afghans with mental disorders are women: officials

Based on last year’s data, 52 percent of people with mental disorders in Afghanistan are women, the Ministry of Public Health said.
However, after the Islamic Emirate took over the country and with the improvement of nationwide security and the provision of better health services, mental disorders have decreased, the ministry said.
“Overall, the mental security of men and women in Afghanistan is not ensured and their mental security is disturbed. According to the figures shared with us, in 2023, 52 percent of the visitors for mental disorders were women,” said Sharaft Zaman Amarkhil, the spokesperson of the Ministry of Public Health.
“Generally speaking, we can say that compared to the past, the instances of mental illnesses have decreased,” he added.
People suffering mental disorders mostly refuse to share their problem, willingly or unwillingly.
“There are many problems at home; We are poor. I finished school, but didn’t find any job,” Ansar, a mentally ill person, said.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), half of Afghanistan’s population suffers from mental distress.
Factors such as unemployment, poverty, domestic violence, ban on girls’ and women’s education and work, and drugs are said to be key contributors to mental distress.
-

 World5 days ago
World5 days agoNorth Korea officials visit Iran in a rare public trip
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days ago‘Serious talent’ Fraser-McGurk bonds with Warner to light up IPL
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoOver 1,000 Afghan refugees forced out of Pakistan in one day
-

 Sport2 days ago
Sport2 days agoAfghanistan beat Iraq 5-3, inch closer to Futsal World Cup berth
-

 Regional2 days ago
Regional2 days agoNew UK sanctions target Iranian drone industry
-

 Regional3 days ago
Regional3 days agoTurkey accuses U.S. of double standards over Gaza in rights report
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoEU allocates 17 million euros to support Afghans on the move
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoPakistan extends registered Afghan refugees’ stay till June 30























