Health
Pig heart transplanted into human patient for the second time
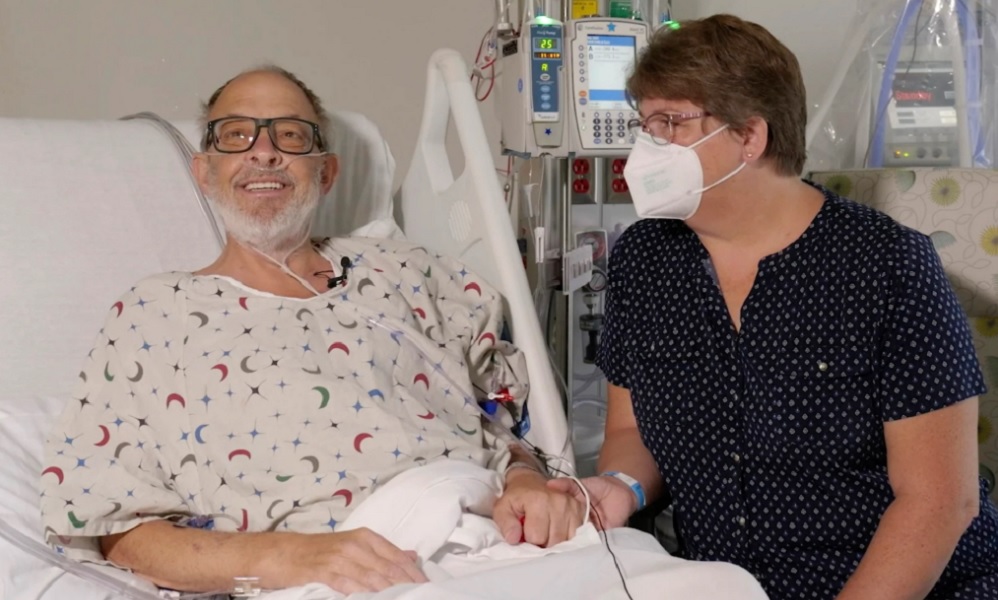
Surgeons have transplanted a pig’s heart into a dying man in a bid to prolong his life – only the second patient to ever undergo such an experimental feat. Two days later, the man was cracking jokes and able to sit in a chair, Maryland doctors said Friday.
The 58-year-old Navy veteran was facing near-certain death from heart failure but other health problems meant he wasn’t eligible for a traditional heart transplant, according to doctors at University of Maryland Medicine, the Associated Press reported.
“Nobody knows from this point forward. At least now I have hope and I have a chance,” Lawrence Faucette, from Frederick, Maryland, said in a video recorded by the hospital before Wednesday’s operation. “I will fight tooth and nail for every breath I can take.”
While the next few weeks will be critical, doctors were thrilled at Faucette’s early response to the pig organ.
“You know, I just keep shaking my head – how am I talking to someone who has a pig heart?” Dr. Bartley Griffith, who performed the transplant, told The Associated Press. He said doctors are feeling “a great privilege but, you know, a lot of pressure.”
The same Maryland team last year performed the world’s first transplanet of a genetically modified pig heart into another dying man, David Bennett, who survived just two months.
There’s a huge shortage of human organs donated for transplant. Last year, there were just over 4,100 heart transplants in the U.S., a record number but the supply is so tight that only patients with the best chance of long-term survival get offered one.
Attempts at animal-to-human organ transplants have failed for decades, as people’s immune systems immediately destroyed the foreign tissue. Now scientists are trying again using pigs genetically modified to make their organs more humanlike.
Recently, scientists at other hospitals have tested pig kidneys and hearts in donated human bodies, hoping to learn enough to begin formal studies of what are called xenotransplants.
To make this new attempt in a living patient outside of a rigorous trial, the Maryland researchers required special permission from the Food and Drug Administration, under a process reserved for certain emergency cases with no other options.
It took over 300 pages of documents filed with FDA, but the Maryland researchers made their case that they’d learned enough from their first attempt last year – even though that patient died for reasons that aren’t fully understood – that it made sense to try again.
And Faucette, who retired as a lab technician at the National Institutes of Health, had to agree that he understood the procedure’s risks.
In a statement his wife, Ann Faucette, said: “We have no expectations other than hoping for more time together. That could be as simple as sitting on the front porch and having coffee together.”
What’s different this time: Only after last year’s transplant did scientists discover signs of a pig virus lurking inside the heart – and they now have better tests to look for hidden viruses. They also made some medication changes.
Possibly more important, while Faucette has end-stage heart failure and was out of other options, he wasn’t as near death as the prior patient.
By Friday, his new heart was functioning well without any supportive machinery, the hospital said.
“It’s just an amazing feeling to see this pig heart work in a human,” said Dr. Muhammad Mohiuddin, the Maryland team’s xenotransplantation expert. But, he cautioned, “we don’t want to predict anything. We will take every day as a victory and move forward.”
This kind of single-patient “compassionate use” can provide some information about how the pig organ works but not nearly as much as more formal testing, said Karen Maschke, a research scholar at the Hastings Center who is helping develop ethics and policy recommendations for xenotransplant clinical trials. That FDA allowed this second case “suggests that the agency is not ready to permit a pig heart clinical trial to start,” Mashke added.
The pig heart, provided by Blacksburg, Virginia-based Revivicor, has 10 genetic modifications – knocking out some pig genes and adding some human ones to make it more acceptable to the human immune system.
Health
Nationwide polio vaccination campaign kicks off across Afghanistan
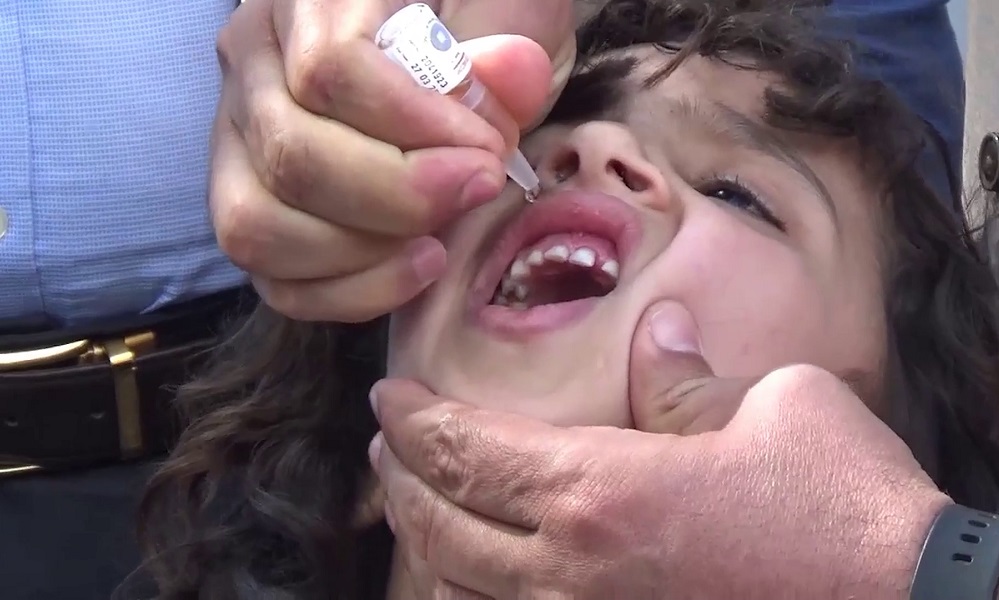
Afghanistan launched a polio vaccination campaign on Monday aimed at protecting around 10.72 million children under the age of 5, the Health Ministry announced.
The four-day campaign will cover 31 of the country’s 34 provinces.
Vaccinations in Ghor, Daikundi and Bamiyan provinces will be implemented later due to recent rains and cold weather, the ministry said in a statement.
“Together with our partners, we are committed to eradicating polio from Afghanistan,” said Dr Qalandar Ebad, the acting minister of public health.
“We will work tirelessly and continue polio vaccination campaigns and complementary health services until we reach the goal of fully eradicating polio.”
The ministry urged religious scholars and local elders to cooperate with vaccine providers to fight polio, a debilitating disease that can lead to paralysis and death.
In December, the World Health Organization (WHO) warned that the repatriation of migrants from neighboring Pakistan has increased the risk of spreading the virus. Since then, Afghanistan has conducted at least three rounds of nationwide vaccinations.
Vaccination campaigns in Afghanistan and Pakistan often face challenges due to conspiracy theories that polio vaccines cause infertility or that vaccinators are spies.
Health
Azerbaijan urged to help improve capacity of Afghan health workers
Acting Minister of Public Health Qalandar Ebad, in a meeting with Azerbaijan’s ambassador, Ilham Mohammadov, called for the country’s assistance in improving the capacity of Afghanistan’s health workers.
The two sides also discussed cooperation in the health sector, capacity building of Afghan health workers, and Azerbaijan’s role in the health sector and other issues, according to a statement released by the Public Health Ministry.
Azerbaijan’s envoy said that his country seeks to cooperate with Afghanistan in a sustainable manner in the field of health.
In other news, the foundation stone for the construction of oxygen production facility was laid at the Indira Gandhi children hospital in Kabul.
Officials of the Ministry of Public Health said that the facility will be built with the financial and technical assistance of the World Health Organization, and with the capacity to produce 200 cylinders of oxygen daily to meet not only the needs of the hospital, but also other health facilities.
Health
Balkh health officials report sharp increase in number of cancer patients
Balkh Public Health Department officials say there has been a significant increase in the number of patients with cancer in the province.
“In 1401, about 2,613 OPD (out patient department) cases were registered with us. In 1402, these figures were 4,912 cases,” said Ehsanullah Kaliwal, the head of the oncology department at Balkh Regional Hospital.
Some doctors say genetic factors, environmental pollution, arbitrary use of medicines, and excessive consumption of meat were reasons for the sharp increase.
One doctor said cancer was also hereditry.
However, a large percentage of cancer patients in Balkh have stomach cancer. Many of them have appealed for the government to improve treatment facilities.
According to health officials, in the first month of this solar year (April), 423 cancer patients visited this hospital for treatment.
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoAfghanistan beat Iraq 5-3, inch closer to Futsal World Cup berth
-

 Regional4 days ago
Regional4 days agoNew UK sanctions target Iranian drone industry
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoEU allocates 17 million euros to support Afghans on the move
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoPakistan extends registered Afghan refugees’ stay till June 30
-

 World5 days ago
World5 days agoUS student protests over Gaza intensify despite arrests
-

 Regional3 days ago
Regional3 days agoChina to host Hamas, Fatah for Palestinian unity talks
-

 Sport2 days ago
Sport2 days agoAfghanistan qualify for FIFA Futsal World Cup for first time ever
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoTripartite trade meeting held in Kabul to boost regional connectivity


























