Health
AFDA orders quality control tests on all imported food and drugs

Afghanistan Food and Drug Authority (AFDA) says foodstuff and medicines will only be allowed to enter the country through customs once quality control tests have been carried out.
Abdul Bari Omar, Director of AFDA, said in a meeting in Kabul that one of the goals of this department is to provide people with access to better quality food, and standard drugs.
Omar also said that in the near future, the export of medicine from Afghanistan to countries abroad will start soon. He said the authority has also developed a procedure that prevents the smuggling of medicines into the country.
AFDA officials added that over the past 18 months, they have issued licenses to 10 factories and destroyed more than 342 tons of low-quality food.
According to AFDA, during this period, there has been a serious fight against drug smuggling, and laboratories will also start working to separate halal from haram.
In addition, the Deputy Minister of Industry and Commerce Qudratullah Jamal said at the meeting that Afghanistan now manufactures 50 different medicines and the hope is that this figure will total 100 by the end of the year.
He has asked businessmen and investors to invest in the pharmaceutical industry in the country.
The people of Afghanistan meanwhile spend $500 million annually on medical treatment abroad due to the poor standard of healthcare across the country.
Health
Azerbaijan urged to help improve capacity of Afghan health workers
Acting Minister of Public Health Qalandar Ebad, in a meeting with Azerbaijan’s ambassador, Ilham Mohammadov, called for the country’s assistance in improving the capacity of Afghanistan’s health workers.
The two sides also discussed cooperation in the health sector, capacity building of Afghan health workers, and Azerbaijan’s role in the health sector and other issues, according to a statement released by the Public Health Ministry.
Azerbaijan’s envoy said that his country seeks to cooperate with Afghanistan in a sustainable manner in the field of health.
In other news, the foundation stone for the construction of oxygen production facility was laid at the Indira Gandhi children hospital in Kabul.
Officials of the Ministry of Public Health said that the facility will be built with the financial and technical assistance of the World Health Organization, and with the capacity to produce 200 cylinders of oxygen daily to meet not only the needs of the hospital, but also other health facilities.
Health
Balkh health officials report sharp increase in number of cancer patients
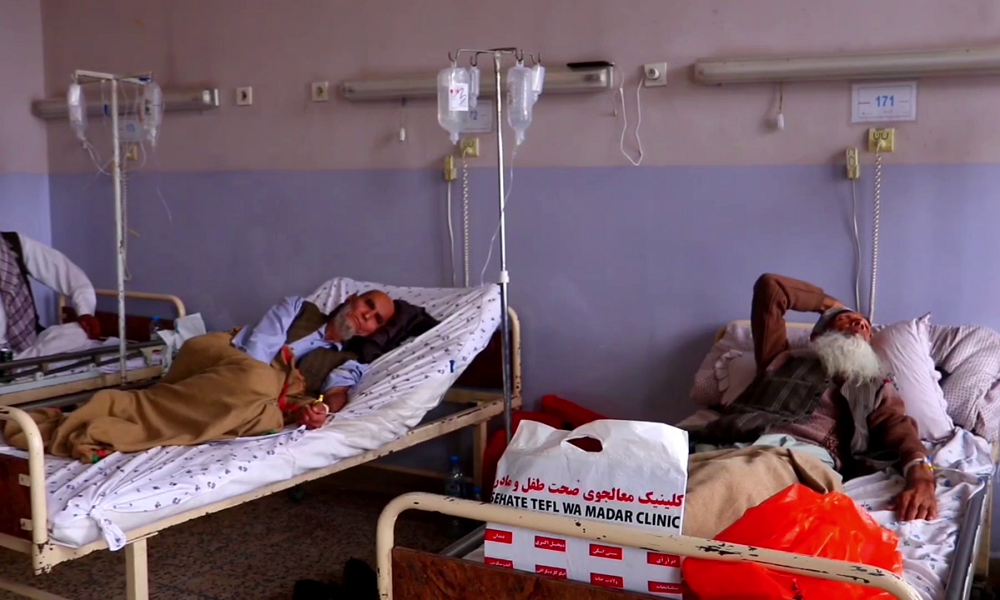
Balkh Public Health Department officials say there has been a significant increase in the number of patients with cancer in the province.
“In 1401, about 2,613 OPD (out patient department) cases were registered with us. In 1402, these figures were 4,912 cases,” said Ehsanullah Kaliwal, the head of the oncology department at Balkh Regional Hospital.
Some doctors say genetic factors, environmental pollution, arbitrary use of medicines, and excessive consumption of meat were reasons for the sharp increase.
One doctor said cancer was also hereditry.
However, a large percentage of cancer patients in Balkh have stomach cancer. Many of them have appealed for the government to improve treatment facilities.
According to health officials, in the first month of this solar year (April), 423 cancer patients visited this hospital for treatment.
Health
Majority of Afghans with mental disorders are women: officials

Based on last year’s data, 52 percent of people with mental disorders in Afghanistan are women, the Ministry of Public Health said.
However, after the Islamic Emirate took over the country and with the improvement of nationwide security and the provision of better health services, mental disorders have decreased, the ministry said.
“Overall, the mental security of men and women in Afghanistan is not ensured and their mental security is disturbed. According to the figures shared with us, in 2023, 52 percent of the visitors for mental disorders were women,” said Sharaft Zaman Amarkhil, the spokesperson of the Ministry of Public Health.
“Generally speaking, we can say that compared to the past, the instances of mental illnesses have decreased,” he added.
People suffering mental disorders mostly refuse to share their problem, willingly or unwillingly.
“There are many problems at home; We are poor. I finished school, but didn’t find any job,” Ansar, a mentally ill person, said.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), half of Afghanistan’s population suffers from mental distress.
Factors such as unemployment, poverty, domestic violence, ban on girls’ and women’s education and work, and drugs are said to be key contributors to mental distress.
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoRashid Khan named AWCC’s brand ambassador
-

 Regional4 days ago
Regional4 days agoIranian president lands in Pakistan for three-day visit to mend ties
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoKolkata beat Bengaluru by one run in IPL as Kohli fumes at dismissal
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoACL: Aino Mina 3-0 Istiqlal Kabul; Attack Energy 3-0 Khadim
-

 Climate Change4 days ago
Climate Change4 days agoRescuers race to reach those trapped by floods in China’s Guangdong
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoAfghanistan, Kazakhstan to hold joint expo in Kabul
-

 World3 days ago
World3 days agoMalaysian navy helicopters collide in mid-air, 10 killed
-

 Sport3 days ago
Sport3 days agoJaiswal ton powers Rajasthan to big IPL win
























