Health
US and Britain roll out campaigns after poliovirus detected in water samples
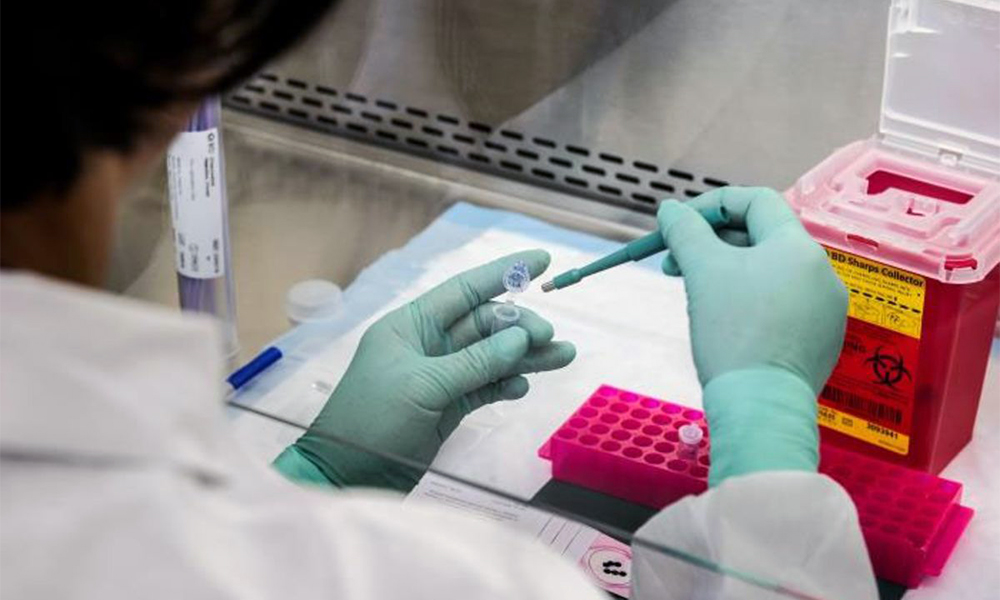
The detection of poliovirus in wastewater samples from New York and London has sparked fears of a possible public health crisis but health experts in the United States believe that the virus is unlikely to secure widespread transmission in the country, especially in highly vaccinated areas.
Medical Daily reported that the US declared the eradication of poliovirus in September 1994, and not many people are aware of the disease it causes and its symptoms at present. There is also limited awareness on how it spreads.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), poliovirus spreads through person-to-person contact and other ways, such as the oral-fecal route and droplets.
Poliovirus is so contagious it can contaminate food and water in unsanitary conditions. Transmission is inevitable when a person makes contact with the feces from an infected person while infection via droplets from a sneeze or cough is less common, Medical Daily reported.
The CDC noted that an infected person could spread the virus almost immediately before and up to two weeks after the symptoms of the disease appear. Once the virus enters the mouth, it can stay in the intestines for many weeks. Asymptomatic people can still pass the virus to other people and make them sick, the report read.
Last month, the US reported its first case of polio in almost a decade.
Meanwhile, Britain rolled out urgent polio vaccinations this week for all London-based children below 10 after the discovery of polio traces in sewage samples across several London boroughs. The move was made after the detection of polio in wastewater samples from New York, London and even Israel sparked fears of a wider outbreak.
Among the symptoms of polio, paralysis is the one most commonly associated with the disease since it can lead to permanent disability or even death. Scientific data showed between 2 and 10 out of 200 infected people develop paralysis and die because the virus can significantly impact the muscles used for breathing.
Since there is no cure or specific treatment for paralytic polio, patients rely on long-term physical or occupational therapy to help them with arm or leg weakness.
Health
Afghanistan faces acute shortage of specialist doctors, officials urge ethics and expansion of health services
Noor Jalal Jalali, the Minister of Public Health, said the ministry is making sustained and intensive efforts to address the gap and expand access to healthcare services in remote and underserved areas of the country.

Afghanistan is continuing to face a serious shortage of specialist doctors, health officials said during the graduation ceremony of specialist physicians from the General Directorate of Medical Specialization for the year 1404.
Noor Jalal Jalali, the Minister of Public Health, said the ministry is making sustained and intensive efforts to address the gap and expand access to healthcare services in remote and underserved areas of the country.
According to Jalali, hospitals are still absent across 318 districts nationwide. He added that initial construction work for hospitals has been completed in 100 of these areas, stressing that strengthening health infrastructure and training qualified specialists remain top priorities for the ministry.
Jalali also called on doctors and health officials to uphold their professional and religious responsibilities by treating patients with compassion, dignity, and good conduct. He emphasized that medical practice should not be driven by material gain, but by the pursuit of public service and the well-being of the people.
Speaking at the same ceremony, Hamdullah Nomani, Minister of Communications and Information Technology noted a decline in public trust toward some medical professionals, saying that despite the presence of many committed and ethical doctors, the behavior of a few motivated solely by financial gain has undermined patient confidence. He urged newly graduated specialists to serve with sincerity and restore public trust in Afghanistan’s healthcare system.
Meanwhile, Abdul Wali Sadiqi, the financial and administrative deputy minister of public health, advised graduates to remain committed to their profession, fulfill their responsibilities honestly, and serve the public with dedication. He stressed that efforts in national service should match those made in personal affairs.
In addition, Abdul Baqi Haqqani, head of the National Examinations Authority, highlighted that humans carry two fundamental responsibilities: worship of Allah and preservation of health, underscoring the vital role doctors play in safeguarding public health.
Health sector experts say Afghanistan now needs skilled and professional medical personnel more than ever, calling for increased investment in specialist training and healthcare infrastructure to meet the country’s growing needs.
Health
Afghan delegation heads to Turkey for medicine talks

Naemullah Ayoubi, Director General of Drug and Health Products Regulation at Afghanistan’s Ministry of Public Health, has departed for Turkey on an official visit accompanied by a technical delegation.
The Ministry of Public Health said the delegation will hold meetings with officials from Turkey’s pharmaceutical regulatory authority and discuss a number of key issues related to the regulation of medicines and health products.
The delegation is also scheduled to visit several pharmaceutical manufacturing factories in Turkey.
According to the ministry, the visit aims to strengthen coordination between the two countries in the production and import of medicines, in order to ensure the availability of high-quality and affordable pharmaceuticals for people in Afghanistan in both the short and long term.
Health
Afghanistan opens first national cancer diagnosis and treatment hospital

The Ministry of Public Health announced on Thursday that Afghanistan has inaugurated its first national hospital dedicated to the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, marking a major step forward in the country’s healthcare services.
The facility, named the National Cancer Diagnostic and Therapeutic Hospital, has officially begun operations and will provide specialized care for cancer patients across the country.
Speaking at the inauguration ceremony, Public Health Minister Noor Jalal Jalali said the 200-bed hospital aims to offer hope and improved treatment options for patients suffering from cancer.
“Fortunately, we are jointly opening a 200-bed hospital for cancer patients, and we hope that this hospital will become a source of hope and healing for those in need,” Jalali said.
The minister added that specialized training programs will soon be launched at the hospital to educate and train domestic medical specialists. He noted that reforms have already been implemented to improve facilities and ensure better healthcare services.
Jalali also emphasized international cooperation in the project, saying that radiotherapy services will be introduced at the hospital with support from India. According to the ministry, India has so far provided $1 million in assistance, including 10 tons of medicines and medical equipment, to support cancer treatment in Afghanistan.
The opening of the hospital is expected to reduce the need for Afghan patients to seek costly cancer treatment abroad and improve access to specialized care inside the country.
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoProminent Muslim scholar issues fatwa calling for Afghanistan-Pakistan ceasefire
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoAfghanistan steps in to replace Iran in supplying fruits and vegetables to Russia
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoMinistry of Public Works: Railway transport operating smoothly across all ports
-

 Sport5 days ago
Sport5 days agoACB names squads for white-ball series against Sri Lanka; Ibrahim Zadran appointed T20I captain
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoInternational Women’s Day: Khalilzad urges IEA to allow girls’ education
-

 Regional5 days ago
Regional5 days agoIranian sailors recovering in Sri Lankan hospital after US submarine attack
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoAfghanistan’s Virtue Ministry: Over 3,400 women’s rights complaints addressed in 10 months
-
 Latest News4 days ago
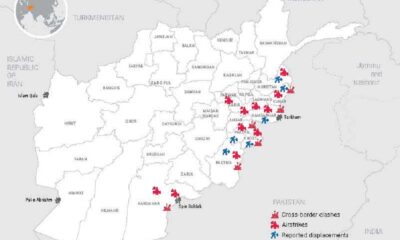
Latest News4 days agoAirstrikes and clashes displace thousands as Afghanistan–Pakistan tensions escalate: UN
























