Science & Technology
China launches historic mission to retrieve samples from far side of the moon
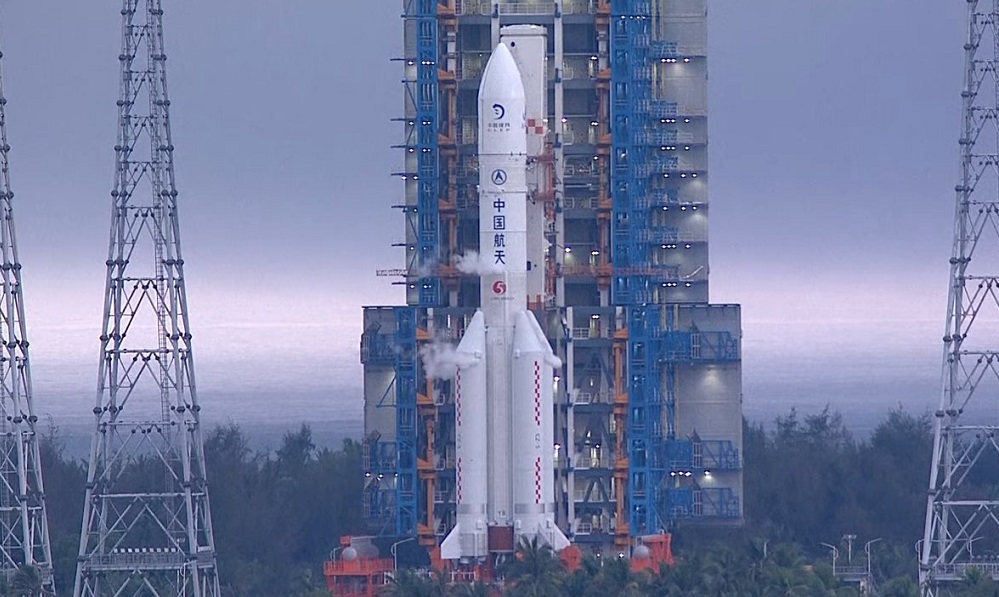
China on Friday launched an uncrewed spacecraft on a nearly two-month mission to retrieve rocks and soil from the far side of the moon, the first country to make such an ambitious attempt.
The Long March-5, China’s largest rocket, blasted off at 5:27 p.m. Beijing time (0927 GMT) from Wenchang Space Launch Center on the southern island of Hainan with the more than 8 metric ton Chang’e-6 probe.
Chang’e-6 is tasked with landing in the South Pole-Aitken Basin on the far side of the moon, which perpetually faces away from the Earth, after which it will retrieve and return samples.
The launch marks another milestone in China’s lunar and space exploration programme.
“It is a bit of a mystery to us how China has been able to develop such an ambitious and successful programme in such a short time,” said Pierre-Yves Meslin, a French researcher working on one of the scientific objectives of the Chang’e-6 mission.
In 2018, Chang’e-4 gave China its first unmanned moon landing, also on the far side. In 2020, Chang’e-5 marked the first time humans retrieved lunar samples in 44 years, and Chang’e-6 could make China the first country to retrieve samples from the moon’s “hidden” side.
FOREIGN PAYLOADS
The launch was attended by scientists, diplomats and space agency officials from France, Italy, Pakistan, and the European Space Agency, all of which have moon-studying payloads aboard Chang’e-6.
But no U.S. organisations applied to get a payload spot, according to Ge Ping, deputy director of the China National Space Administration’s (CNSA) Lunar Exploration and Space Program.
China is banned by U.S. law from any collaboration with the U.S. space agency, NASA.
“The far side of the moon has a mystique perhaps because we literally can’t see it, we have never seen it apart from with robotic probes or the very few number of humans that have been around the other side,” said Neil Melville-Kenney, a technical officer at ESA working with Chinese researchers on one of the Chang’e-6 payloads.
After the probe separates from the rocket, it will take four to five days to reach the moon’s orbit. In early June a few weeks later, it will land.
Once on the moon, the probe will spend two days digging up 2 kilogrammes (4.4 lb) of samples before returning to Earth, where it is expected to land in Inner Mongolia.
The window for the probe to collect samples on the far side is 14 hours, compared to 21 hours for the near side.
The samples brought back by Chang’e-5 allowed Chinese scientists to uncover new details about the moon, including more accurately dating the timespan of volcanic activity on the moon, as well as a new mineral.
Ge said the scientific value of Chang’e-6 lay in the geological age of the South Pole-Aitken Basin, which his team estimated was about 4 billion years, much older than the samples previously brought back by the Soviet Union and the United States, which were about 3 billion years old, as well as the 2-billion-year-old samples from Chang’e-5.
LUNAR BASE
Besides uncovering new information about the celestial body closest to Earth, Chang’e-6 is part of a long-term project to build a permanent research station on the moon: the China and Russia-led International Lunar Research Station (ILRS).
The construction of such a station would provide an outpost for China and its partners to pursue deep space exploration.
“We know that the moon may have resources that could become useful in the future, so the European Space Agency, NASA, the Chinese agency and others around the world are going to the moon,” said James Carpenter, head of the ESA’s lunar science office.
“Part of the rationale is to understand those resources,” Carpenter said.
Wu Weiren, chief designer of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Project, speaking at the 2024 China Space Conference last month, said a “basic model” of the ILRS would be built by 2035.
(Reuters)
Science & Technology
Russia plans a nuclear power plant on the moon within a decade

Russia plans to put a nuclear power plant on the moon in the next decade to supply its lunar space programme and a joint Russian-Chinese research station, as major powers rush to explore the earth’s only natural satellite.
Ever since Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin became the first human to go into space in 1961, Russia has prided itself as a leading power in space exploration, but in recent decades it has fallen behind the United States and, increasingly, China, Reuters reported.
Russia’s ambitions suffered a massive blow in August 2023 when its unmanned Luna-25 mission smashed into the surface of the moon while attempting to land, and Elon Musk has revolutionised the launch of space vehicles – once a Russian speciality.
IS THAT A NUCLEAR REACTOR ON THE MOON?
Russia’s state space corporation, Roscosmos, said in a statement that it planned to build a lunar power plant by 2036 and signed a contract with the Lavochkin Association aerospace company to do it.
Roscosmos did not say explicitly that the plant would be nuclear but it said the participants included Russian state nuclear corporation Rosatom and the Kurchatov Institute, Russia’s leading nuclear research institute.
Roscosmos said the purpose of the plant was to power Russia’s lunar programme, including rovers, an observatory and the infrastructure of the joint Russian-Chinese International Lunar Research Station.
“The project is an important step towards the creation of a permanently functioning scientific lunar station and the transition from one-time missions to a long-term lunar exploration programme,” Roscosmos said.
The head of Roscosmos, Dmitry Bakanov, said in June that one of the corporation’s aims was to put a nuclear power plant on the moon and to explore Venus, known as earth’s “sister” planet.
The moon, which is 384,400 km (238,855 miles) from our planet, moderates the earth’s wobble on its axis, which ensures a more stable climate. It also causes tides in the world’s oceans.
U.S. ALSO PLANS A REACTOR ON THE MOON
Russia is not the only one with such plans. NASA in August declared its intent to put a nuclear reactor on the moon by the first quarter of fiscal year 2030.
“We’re in a race to the moon, in a race with China to the moon. And to have a base on the moon, we need energy,” U.S. Transport Secretary Sean Duffy said in August, when asked about the plans.
He added that the United States was currently behind in the race to the moon. He said energy was essential to allow life to be sustained on the moon and thence for humans to get to Mars.
International rules ban putting nuclear weapons in space but there are no bans on putting nuclear energy sources into space – as long as they comply with certain rules.
Some space analysts have predicted a lunar gold rush: NASA says there are estimates of a million tonnes of Helium-3, an isotope of helium that is rare on earth, on the moon.
Rare earth metals – used in smartphones, computers and advanced technologies – are also present on the moon, including scandium, yttrium and the 15 lanthanides, according to research by Boeing.
Science & Technology
Australia social media ban set to take effect, sparking a global crackdown
For the social media businesses, the implementation marks a new era of structural stagnation as user numbers flatline and time spent on platforms shrinks, studies show.

Australia is set to become the first country to implement a minimum age for social media use on Wednesday, with platforms like Instagram, TikTok and YouTube forced to block more than a million accounts, marking the beginning of an expected global wave of regulation.
From midnight, 10 of the biggest platforms will be required to block Australians aged under 16 or be fined up to A$49.5 million ($33 million), Reuters reported.
The law received harsh criticism from major technology companies and free speech advocates, but was praised by parents and child advocates.
The rollout closes out a year of speculation about whether a country can block children from using technology that is built into modern life. And it begins a live experiment that will be studied globally by lawmakers who want to intervene directly because they are frustrated by what they say is a tech industry that has been too slow to implement effective harm-minimisation efforts.
Governments from Denmark to Malaysia – and even some states in the U.S., where platforms are rolling back trust and safety features – say they plan similar steps, four years after a leak of internal Meta (META.O) documents showed the company knew its products contributed to body image problems and suicidal thoughts among teenagers while publicly denying the link existed.
“While Australia is the first to adopt such restrictions, it is unlikely to be the last,” said Tama Leaver, a professor of internet studies at Curtin University.
“Governments around the world are watching how the power of Big Tech was successfully taken on. The social media ban in Australia … is very much the canary in the coal mine.”
A spokesperson for the British government, which in July began forcing websites hosting pornographic content to block under-18 users, said it was “closely monitoring Australia’s approach to age restrictions.”
“When it comes to children’s safety, nothing is off the table,” they added.
Few will scrutinise the impact as closely as the Australians. The eSafety Commissioner, an Australian regulator tasked with enforcing the ban, hired Stanford University and 11 academics to analyse data on thousands of young Australians covered by the ban for at least two years.
Though the ban covers 10 platforms initially, including Alphabet’s (GOOGL.O), YouTube, Meta’s Instagram and TikTok, the government has said the list will change as new products appear and young users switch to alternatives.
Of the initial 10, all but Elon Musk’s X have said they will comply using age inference – guessing a person’s age from their online activity – or age estimation, which is usually based on a selfie. They might also check with uploaded identification documents or linked bank account details.
Musk has said the ban “seems like a backdoor way to control access to the internet by all Australians” and most platforms have complained that it violates people’s right to free speech.
For the social media businesses, the implementation marks a new era of structural stagnation as user numbers flatline and time spent on platforms shrinks, studies show.
Platforms say they don’t make much money showing advertisements to under-16s, but they add that the ban interrupts a pipeline of future users. Just before the ban took effect, 86% of Australians aged 8 to 15 used social media, the government said.
“The days of social media being seen as a platform for unbridled self-expression, I think, are coming to an end,” said Terry Flew, the co-director of University of Sydney’s Centre for AI, Trust and Governance.
Platforms responded to negative headlines and regulatory threats with measures like a minimum age of 13 and extra privacy features for teenagers, but “if that had been the structure of social media in the boom period, I don’t think we’d be having this debate,” he added.
Science & Technology
Ethiopian volcano erupts for first time in nearly 12,000 years
Ash from the eruption drifted across the region, spreading over Yemen, Oman, India, and parts of Pakistan.
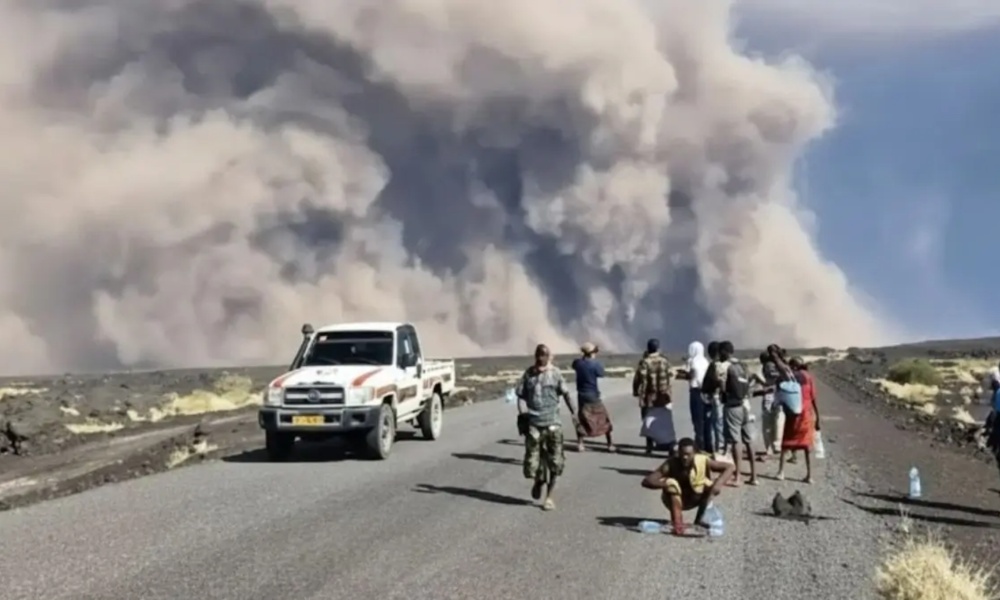

The Hayli Gubbi volcano in Ethiopia’s Afar region has erupted for the first time in almost 12,000 years, sending massive ash plumes soaring up to 14 kilometres into the atmosphere, according to the Toulouse Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre.
The eruption began on Sunday and lasted several hours. Hayli Gubbi, located around 800 kilometres northeast of Addis Ababa near the Eritrean border, sits within the geologically active Rift Valley, where two major tectonic plates meet. The volcano rises roughly 500 metres above the surrounding landscape.
Ash from the eruption drifted across the region, spreading over Yemen, Oman, India, and parts of Pakistan. Satellite imagery and social-media videos captured a towering column of white smoke billowing into the sky.
The Smithsonian Institution’s Global Volcanism Program notes that Hayli Gubbi has no recorded eruptions during the Holocene, the period dating back about 12,000 years to the end of the last Ice Age.
Volcanologist Simon Carn of Michigan Technological University also confirmed on Bluesky that the volcano had “no record of Holocene eruptions.”
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoAfghanistan exports 10 containers of batteries to Saudi Arabia and UAE for first time
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoPakistani cleric condemns lifetime immunity for Army Chief as un-Islamic
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoAfghanistan signs 30-year deal for marble mining in Daikundi
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoBush Institute criticizes Trump administration’s Afghan immigration freeze
-

 International Sports2 days ago
International Sports2 days agoAriana News to broadcast key AFC Champions League Two clash
-

 Regional3 days ago
Regional3 days agoPakistan agrees to $4 billion arms deal with Libyan National Army
-

 Health2 days ago
Health2 days agoAfghan Health Minister hails India visit as new chapter in bilateral ties
-

 Latest News1 day ago
Latest News1 day agoPakistan’s actions target militants, not religious sites: Khawaja Asif























