Science & Technology
North Korea to launch satellites to monitor U.S. and its allies
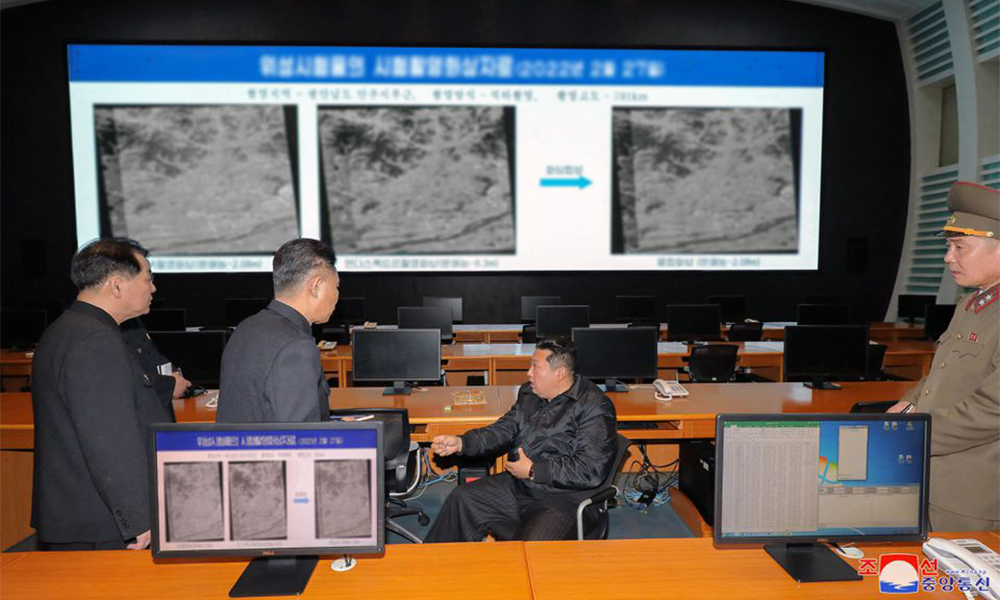
North Korea will launch a number of reconnaissance satellites in coming years to provide real-time information on military actions by the United States and its allies, state media on Thursday reported leader Kim Jong Un as saying.
While inspecting North Korea’s National Aerospace Development Administration, Kim said “a lot” of military reconnaissance satellites would be put into sun-synchronous polar orbit in the period of a five-year plan announced last year, state news agency KCNA reported.
“He noted that the purpose of developing and operating the military reconnaissance satellite is to provide the armed forces of the DPRK with real-time information on military actions against it by the aggression troops of the U.S. imperialism and its vassal forces in south Korea, Japan and the Pacific,” the news agency said.
North Korea appears to be preparing to launch a reconnaissance satellite, which could prove as controversial as the nuclear-armed country’s weapons tests because they use the same banned ballistic missile technology, experts say.
North Korea says it conducted two tests of satellite systems on Feb. 27 and March 5. Authorities in South Korea, Japan, and the United States says the tests involved launches of ballistic missiles.
The launches drew international condemnation and the U.S. military said on Thursday it had increased surveillance and reconnaissance collection in the Yellow Sea.
The United States also said it had heightened its ballistic missile defence readiness after a “significant increase” in North Korean missile tests.
Kim defended the satellite work as not only about gathering information but protecting North Korea’s sovereignty and national interests, exercising its legitimate rights to self-defence, and elevating national prestige, KCNA reported.
“He stressed that this urgent project for perfecting the country’s war preparedness capacity by improving our state’s war deterrent is the supreme revolutionary task, a political and military priority task to which our Party and government attach the most importance,” KCNA said.
The United States and its allies have condemned previous North Korean space launches as violations of U.N. Security Council resolutions that have imposed sanctions on North Korea over its nuclear and missile programmes.
North Korea has not tested a nuclear weapon or its long-range intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) since 2017, but has suggested in could resume such tests because talks with the United States are stalled.
Its latest flurry of missile launches could be groundwork for a return to ICBM and nuclear bomb tests this year, the U.S. Directorate of National Intelligence (DNI) said in its annual Worldwide Threat Assessment released this week.
A satellite launched into orbit would be the first since 2016.
Recent sub-orbital launches, which likely used road-mobile medium-range ballistic missiles, appeared designed to “pop the key components of an imagery reconnaissance satellite up to operational altitudes for a few minutes of testing”, 38 North, a U.S.-based monitoring group, said in a report.
Such components, including satellite stabilisation, the imaging payload, and data transmission may have failed in previous tests and therefore required additional testing, the group said.
“It remains to be seen how capable any North Korean imagery satellite would be, the frequency of launches, or how many such satellites might be maintained in orbit at any one time—all key indicators of the actual military significance of such satellites,” 38 North said.
Regardless, North Korea clearly sees this capability as having propaganda value and showcasing its technological prowess and effective leadership, it added.
A launch could make technical contributions to North Korea’s ICBM capability, depending on what type of rocket booster is used, 38 North said.
“It may also be the precursor to other more provocative developments mentioned by Kim, such as the testing of multiple-warhead missiles, solid-propellant ICBMs, and ICBM-range solid-propellant submarine-launched ballistic missiles,” it said.
Science & Technology
Apple loses top phonemaker spot to Samsung as iPhone shipments drop, IDC says

Apple’s (AAPL.O), opens new tab smartphone shipments dropped about 10% in the first quarter of 2024, hurt by intensifying competition by Android smartphone makers aiming for the top spot, data from research firm IDC showed on Sunday.
Global smartphone shipments increased 7.8% to 289.4 million units during January-March, with Samsung (005930.KS), opens new tab, at 20.8% market share, clinching the top phonemaker spot from Apple, Reuters reported.
The iPhone-maker’s steep sales decline comes after its strong performance in the December quarter when it overtook Samsung as the world’s No.1 phone maker. It’s back to the second spot, with 17.3% market share, as Chinese brands such as Huawei gain market share.
Xiaomi, one of China’s top smartphone makers, occupied the third position with a market share of 14.1% during the first quarter, read the report.
South Korea’s Samsung, which launched its latest flagship smartphone lineup – Galaxy S24 series – in the beginning of the year, shipped more than 60 million phones during the period.
Global sales of Galaxy S24 smartphones jumped 8%, compared to last year’s Galaxy S23 series during their first three weeks of availability, data provider Counterpoint previously said.
In the first quarter, Apple shipped 50.1 million iPhones, down from 55.4 million units it shipped same period last year, according to IDC.
Apple’s smartphone shipments in China shrank 2.1% in the final quarter of 2023 from a year earlier.
The drop underscores the challenges facing the U.S. firm in its third biggest market, as some Chinese companies and government agencies limit employees’ use of Apple devices, a measure that mirrors U.S. government restrictions on Chinese apps on security grounds.
The Cupertino, California-based company in June will hold its Worldwide Developers Conference (WWDC), where it will highlight updates to the software powering iPhones, iPads, and other Apple devices.
Investors are closely watching for updates on artificial intelligence development at Apple, which has so far spoken little about incorporating the AI technology into its devices. The company earlier this year lost the crown as the world’s most valuable company to Microsoft (MSFT.O), opens new tab, Reuters reported.
Science & Technology
China launch of relay satellite Queqiao-2 for lunar probe mission successful
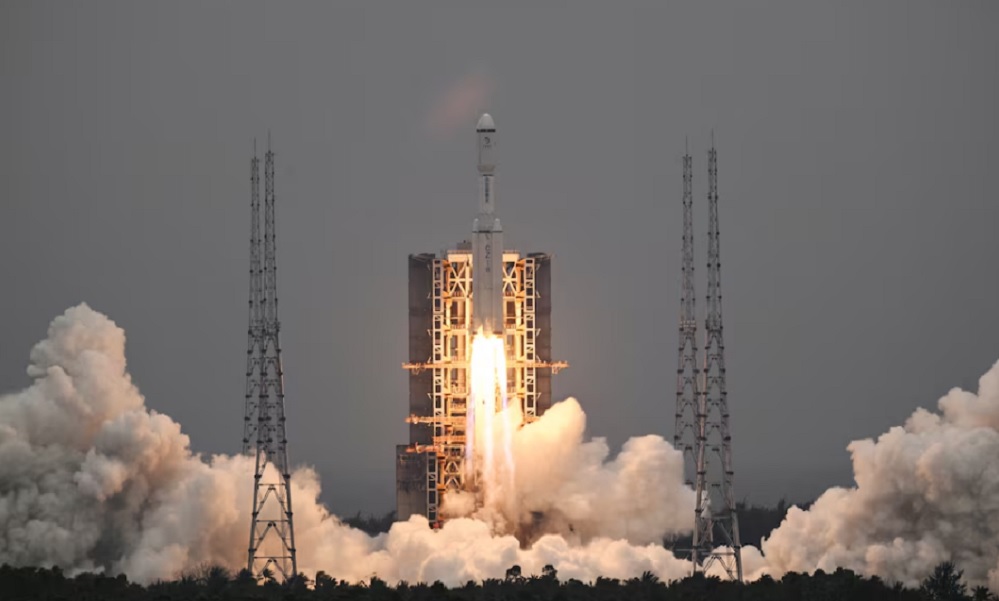

China National Space Administration (CNSA) said on Friday its launch of a key signal relay satellite was a “complete success” and it would serve as the communication bridge for its future lunar probe missions for years to come, state media reported.
China launched the satellite Queqiao-2, which was named after a mythological bridge made of magpies, and two miniature satellites, Tiandu-1 and Tiandu-2, on March 20.
Queqiao-2 will be used as a communications bridge between the ground operations on earth and upcoming lunar probe missions on the far side of the moon until at least 2030.
The moon’s near side always faces earth. That means data transfers from the far side are impossible because there is no direct line of sight.
Queqiao-2 researcher and developer Xiong Liang described the satellite as “the main switch” of the whole fourth phase of lunar missions, according to state television CCTV.
“Only when the main switch is flipped on, all the communications can kick off,” Xiong said.
Queqiao-2 will orbit the moon and relay signals to and from the Chang’e-6 mission, which expected to be launched in May. The robotic Chang’e-6 probe will seek to retrieve samples from an ancient basin, acquiring lunar material from the moon’s hidden side for the first time.
Queqiao-2 will also be used as a relay platform for the Chang’e-7 lunar mission in 2026 and the Chang’e-8 mission in 2028.
The functions and performance of Queqiao-2 met mission requirements and it will be able to provide relay communication services for China’s lunar exploration projects and future lunar missions for China and other countries, said the CNSA, according to CCTV.
Queqiao-2 entered its targeted elliptical orbit on April 2 after a correction midway, near-moon braking and orbital manoeuvre around the moon, CNSA said.
The satellite has successfully communicated with Chang’e 4, which was the first spacecraft to perform a soft landing on the far side of the moon and is still carrying out its exploration mission. It also communicated with the Chang’e-6 probe while it is still on the ground earlier this month.
The successful launch of Queqiao-2 comes after the failed launch of another lunar spacecraft DRO-A/B satellites, which was intended to enter the moon’s distant retrograde orbit (DRO).
China has not released any information on whether or not the satellites can be retrieved.
(Reuters)
Science & Technology
Russia aborts planned test launch of new heavy-lift space rocket
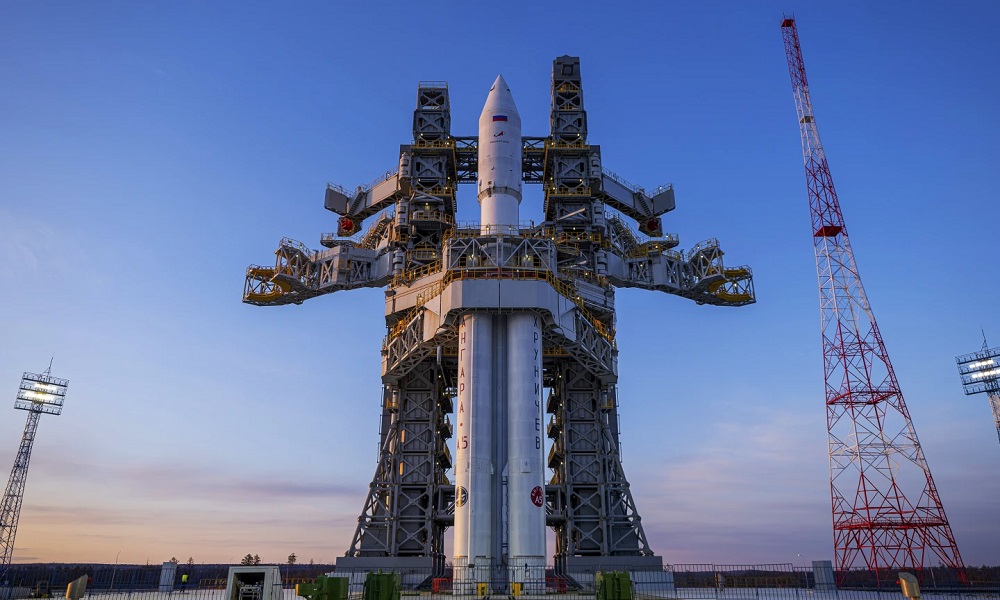

Russian space officials on Tuesday aborted the test launch of a new heavy-lift rocket from its far-eastern launch pad.
The Angara-A5 rocket was scheduled to lift off from the Vostochny space launch facility at 0900 GMT Tuesday, but the launch was aborted two minutes before, AP reported.
Yuri Borisov, head of Roscosmos state space corporation, said the automatic safety system canceled the launch after registering a flaw in the oxidizer tank pressurization system.
He said the next launch attempt was set for Wednesday.
Tuesday’s launch was to be the fourth for the Angara-A5, a heavy-lift version of the new Angara family of rockets that has been developed to replace the Soviet-designed Proton rockets.
-

 Sport5 days ago
Sport5 days agoACL fever grows as fixtures finalized
-

 World5 days ago
World5 days agoUS will not take part in any Israeli retaliatory action against Iran
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoOver 50 people dead in traffic accidents over Eid
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoUS identifies Kabul airport suicide bomber
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoAfghanistan-Kazakhstan chamber of commerce opens in Herat
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoGood rains enable DABS to increase power production in Kabul
-

 World4 days ago
World4 days agoIsraeli military vows response to Iran attack as calls for restraint mount
-

 Sport3 days ago
Sport3 days agoATN secures exclusive rights to broadcast Paris 2024 Olympics
























