Science & Technology
Rock collected by Apollo 17 astronaut in 1972 reveals moon’s age

During the Apollo 17 mission in 1972 – the last time people walked on the moon – U.S. astronauts Harrison Schmitt and Eugene Cernan collected about 243 pounds (110.4 kg) of soil and rock samples that were returned to Earth for further study.
A half century later, crystals of the mineral zircon inside a coarse-grained igneous rock fragment collected by Schmitt are giving scientists a deeper understanding about the moon’s formation and the precise age of Earth’s celestial partner, Reuters reported.
The moon is about 40 million years older than previously thought – forming more than 4.46 billion years ago, within 110 million years after the solar system’s birth, scientists said on Monday, based on analyses of the crystals.
The leading hypothesis for lunar formation is that during the solar system’s chaotic early history a Mars-sized object called Theia slammed into primordial Earth. This blasted magma – molten rock – into space, forming a debris disk that orbited Earth and coalesced into the moon. But the exact timing of the moon’s formation has been hard to nail down.
Mineral crystals were able to form after the magma cooled and solidified. The researchers used a method called atom probe tomography to confirm the age of the oldest-known solids that formed after the giant impact, the zircon crystals inside the fragment of a type of rock called norite collected by Schmitt.
“I love the fact that this study was done on a sample that was collected and brought to Earth 51 years ago. At that time, atom probe tomography wasn’t developed yet and scientists wouldn’t have imagined the types of analyses we do today,” said cosmochemist Philipp Heck, senior director of research at the Field Museum in Chicago, a University of Chicago professor and senior author of the study published in the journal Geochemical Perspectives Letter.
“Interestingly, all the oldest minerals found on Earth, Mars and the moon are zircon crystals. Zircon, not diamond, lasts forever,” UCLA planetary scientist and study co-author Bidong Zhang added.
The rock containing the zircon was collected in the Taurus-Littrow valley at the southeastern edge of the lunar Mare Serenitatis (Sea of Serenity) and stored at NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston.
“Zircons are very hard and tough and survive the breakdown of rocks during weathering,” Heck said.
A study led by Zhang published in 2021 used a technique called ion microprobe analysis to measure how many atoms of uranium and lead were in the crystals, calculating the age of the zircon based on the decay of radioactive uranium to lead over time. That age needed to be confirmed through another method because of a potential complication involving lead atoms if defects existed in the zircon crystal structure.
The new study used atom probe tomography to determine there were no complications involving the lead atoms, confirming the age of the crystals.
“I see this as a great example of what the nanoscale, or even atomic scale, can tell us about big-picture questions,” said study lead author Jennika Greer, a cosmochemist at the University of Glasgow in Scotland.
The moon, which orbits Earth at an average distance of about 239,000 miles (385,000 km), has a diameter of about 2,160 miles (3,475 km), a bit more than a quarter of our planet’s diameter.
“The giant impact that formed the moon was a cataclysmic event for Earth and changed Earth’s rotational speed. After that, the moon had an effect on stabilizing Earth’s rotational axis and slowing down Earth’s rotational speed,” Heck said. “The formation date of the moon is important as only after that Earth became a habitable planet.”
“The moon helps stabilize Earth’s axis for a stable climate,” Zhang added. “The moon’s gravitational pulls help shape the ocean’s ecosystem. The moon is inspirational to human cultures and explorations. And NASA and other space agencies see the moon as a steppingstone for future deep-space explorations.”
Science & Technology
Australia social media ban set to take effect, sparking a global crackdown
For the social media businesses, the implementation marks a new era of structural stagnation as user numbers flatline and time spent on platforms shrinks, studies show.

Australia is set to become the first country to implement a minimum age for social media use on Wednesday, with platforms like Instagram, TikTok and YouTube forced to block more than a million accounts, marking the beginning of an expected global wave of regulation.
From midnight, 10 of the biggest platforms will be required to block Australians aged under 16 or be fined up to A$49.5 million ($33 million), Reuters reported.
The law received harsh criticism from major technology companies and free speech advocates, but was praised by parents and child advocates.
The rollout closes out a year of speculation about whether a country can block children from using technology that is built into modern life. And it begins a live experiment that will be studied globally by lawmakers who want to intervene directly because they are frustrated by what they say is a tech industry that has been too slow to implement effective harm-minimisation efforts.
Governments from Denmark to Malaysia – and even some states in the U.S., where platforms are rolling back trust and safety features – say they plan similar steps, four years after a leak of internal Meta (META.O) documents showed the company knew its products contributed to body image problems and suicidal thoughts among teenagers while publicly denying the link existed.
“While Australia is the first to adopt such restrictions, it is unlikely to be the last,” said Tama Leaver, a professor of internet studies at Curtin University.
“Governments around the world are watching how the power of Big Tech was successfully taken on. The social media ban in Australia … is very much the canary in the coal mine.”
A spokesperson for the British government, which in July began forcing websites hosting pornographic content to block under-18 users, said it was “closely monitoring Australia’s approach to age restrictions.”
“When it comes to children’s safety, nothing is off the table,” they added.
Few will scrutinise the impact as closely as the Australians. The eSafety Commissioner, an Australian regulator tasked with enforcing the ban, hired Stanford University and 11 academics to analyse data on thousands of young Australians covered by the ban for at least two years.
Though the ban covers 10 platforms initially, including Alphabet’s (GOOGL.O), YouTube, Meta’s Instagram and TikTok, the government has said the list will change as new products appear and young users switch to alternatives.
Of the initial 10, all but Elon Musk’s X have said they will comply using age inference – guessing a person’s age from their online activity – or age estimation, which is usually based on a selfie. They might also check with uploaded identification documents or linked bank account details.
Musk has said the ban “seems like a backdoor way to control access to the internet by all Australians” and most platforms have complained that it violates people’s right to free speech.
For the social media businesses, the implementation marks a new era of structural stagnation as user numbers flatline and time spent on platforms shrinks, studies show.
Platforms say they don’t make much money showing advertisements to under-16s, but they add that the ban interrupts a pipeline of future users. Just before the ban took effect, 86% of Australians aged 8 to 15 used social media, the government said.
“The days of social media being seen as a platform for unbridled self-expression, I think, are coming to an end,” said Terry Flew, the co-director of University of Sydney’s Centre for AI, Trust and Governance.
Platforms responded to negative headlines and regulatory threats with measures like a minimum age of 13 and extra privacy features for teenagers, but “if that had been the structure of social media in the boom period, I don’t think we’d be having this debate,” he added.
Science & Technology
Ethiopian volcano erupts for first time in nearly 12,000 years
Ash from the eruption drifted across the region, spreading over Yemen, Oman, India, and parts of Pakistan.
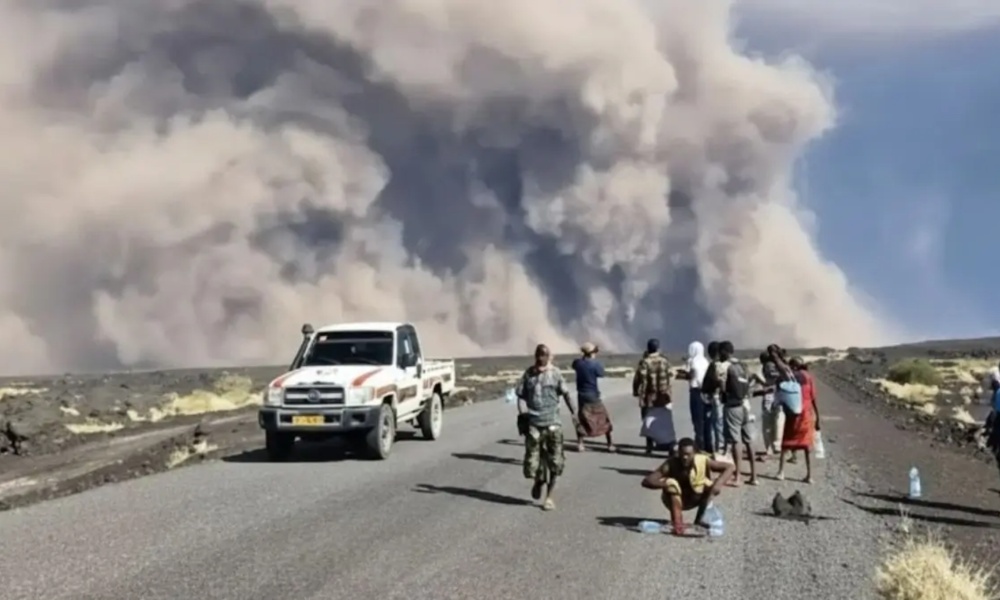

The Hayli Gubbi volcano in Ethiopia’s Afar region has erupted for the first time in almost 12,000 years, sending massive ash plumes soaring up to 14 kilometres into the atmosphere, according to the Toulouse Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre.
The eruption began on Sunday and lasted several hours. Hayli Gubbi, located around 800 kilometres northeast of Addis Ababa near the Eritrean border, sits within the geologically active Rift Valley, where two major tectonic plates meet. The volcano rises roughly 500 metres above the surrounding landscape.
Ash from the eruption drifted across the region, spreading over Yemen, Oman, India, and parts of Pakistan. Satellite imagery and social-media videos captured a towering column of white smoke billowing into the sky.
The Smithsonian Institution’s Global Volcanism Program notes that Hayli Gubbi has no recorded eruptions during the Holocene, the period dating back about 12,000 years to the end of the last Ice Age.
Volcanologist Simon Carn of Michigan Technological University also confirmed on Bluesky that the volcano had “no record of Holocene eruptions.”
Science & Technology
Cloudflare outage easing after millions of internet users affected

A global outage at web-infrastructure firm Cloudflare began to ease on Tuesday afternoon after preventing people from accessing major internet platforms, including X and ChatGPT.
Cloudflare, whose network handles around a fifth of web traffic, said it started to investigate the internal service degradation around 6:40 a.m. ET. It has deployed a fix but some customers might still be impacted as it recovers service.
The incident marked the latest hit to major online services. An outage of Amazon’s cloud service last month caused global turmoil as thousands of popular websites and apps, including Snapchat, were inaccessible due to the disruption.
Cloudflare – whose shares were down about 5% in premarket trading – runs one of the world’s largest networks that helps websites and apps load faster and stay online by protecting them from traffic surges and cyberattacks.
The latest outage prevented users from accessing platforms such as Canva, X, and ChatGPT, prompting users to log outage reports with Downdetector.
Downdetector tracks outages by collating status reports from a number of sources. “We saw a spike in unusual traffic to one of Cloudflare’s services beginning at 11:20 UTC. That caused some traffic passing through Cloudflare’s network to experience errors,” the company said in an emailed statement.
“We are all hands on deck to make sure all traffic is served without errors.”
X and ChatGPT-creator OpenAI did not immediately respond to requests for comment. – REUTERS
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoAfghanistan exports 10 containers of batteries to Saudi Arabia and UAE for first time
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoPakistani cleric condemns lifetime immunity for Army Chief as un-Islamic
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoAfghanistan signs 30-year deal for marble mining in Daikundi
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoAfghan health minister calls for medical cooperation between Kabul and New Delhi
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoKarzai urges reopening of girls’ schools and universities for Afghanistan’s bright future
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoBush Institute criticizes Trump administration’s Afghan immigration freeze
-

 International Sports2 days ago
International Sports2 days agoAriana News to broadcast key AFC Champions League Two clash
-

 Regional2 days ago
Regional2 days agoPakistan agrees to $4 billion arms deal with Libyan National Army