Latest News
Afghanistan on brink of emergency as mass deportations accelerate, UN Warns
The agency warned that a failure to respond quickly and at scale risks triggering widespread displacement, food insecurity, and public health emergencies.
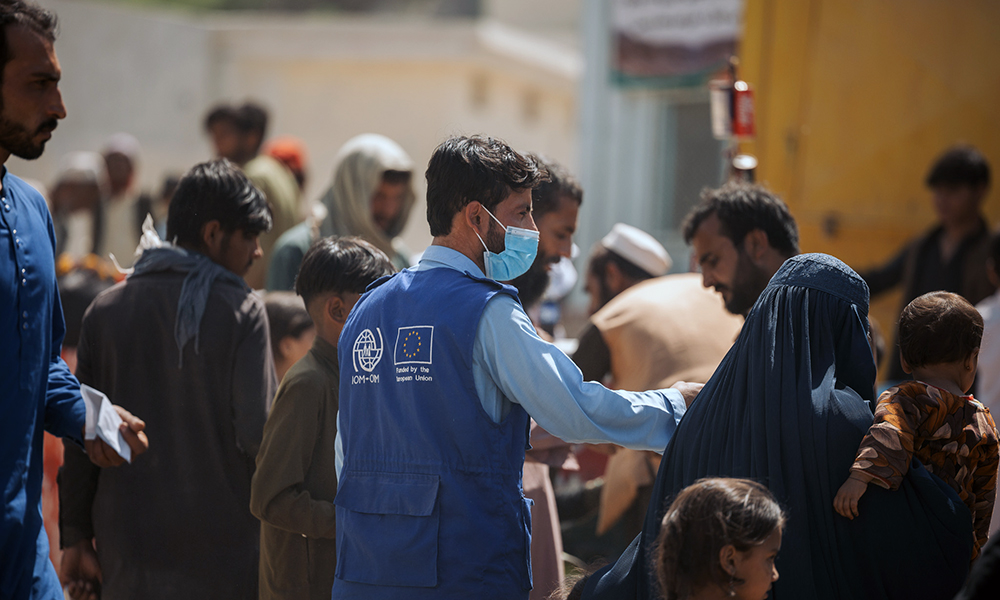

The United Nations Assistance Mission in Afghanistan (UNAMA) has issued a stark warning that the country faces a rapidly unfolding humanitarian emergency due to a dramatic increase in the forced return of Afghan migrants from neighboring countries. Nearly 949,000 Afghans have returned to Afghanistan in the first half of 2025, the agency reported, including 741,000 from Iran and 208,000 from Pakistan.
In an alert published this week, UNAMA emphasized that without immediate and coordinated international support, the sudden influx could overwhelm fragile border communities and spiral into a broader humanitarian catastrophe.
The return rate surged sharply in June, with more than 283,000 individuals deported from Iran—a figure that UNAMA officials say is directly linked to the recent escalation of conflict between Iran and Israel.
As Tehran tightens domestic security and cracks down on undocumented migrants, aid agencies on the Afghan side of the border report scenes of chaos, overcrowding, and severe humanitarian need.
“We are witnessing an unsustainable level of returns that border communities are not equipped to manage,” a senior UNAMA official said. “Without immediate and sustained support, the situation could spiral into a humanitarian disaster.”
Unlike previous waves of returnees—which largely comprised single adult men—over 60% of returnees in 2025 are now families, including women, children, and elderly individuals. Many had lived in Iran or Pakistan for years, and some children have never set foot in Afghanistan.
This shift in demographic has compounded vulnerabilities. Returnees often arrive without shelter, income, documentation, or social ties, and face heightened risks of malnutrition, exposure to disease, and exploitation.
“These are not just returnees. They are people who have nowhere to go,” said one aid worker stationed at the Islam Qala crossing in Herat province. “Many of their villages were destroyed or abandoned during the war. Others are being returned to a country they don’t even recognize.”
Border provinces buckling under pressure
Afghanistan’s western border provinces, particularly Herat and Nimroz, are under extraordinary pressure. With limited access to potable water, electricity, healthcare, and housing, local authorities and humanitarian partners are struggling to accommodate the daily flow of returnees.
Local aid officials have warned of rising tensions between host communities and returnees as competition for food, shelter, and jobs intensifies. In some areas, informal tent settlements have sprung up, with little access to basic services or protection.
In its statement, UNAMA urged donor governments, humanitarian organizations, and international financial institutions to step up their support and immediately mobilize resources.
The agency warned that a failure to respond quickly and at scale risks triggering widespread displacement, food insecurity, and public health emergencies.
The mission also emphasized the need for sustainable reintegration support, including access to education, job creation, psychosocial care, and legal assistance to help returnees rebuild their lives and prevent secondary displacement.
The warning comes as Afghanistan remains gripped by overlapping crises: the long-term effects of conflict, a fragile economy, widespread poverty, and minimal diplomatic recognition under the Islamic Emirate-led government. According to the UN, 28.3 million people—over two-thirds of the population—will require humanitarian assistance in 2025.
International funding for Afghan aid efforts has declined in recent years, with many donor governments limiting engagement due to political tensions with the IEA. As a result, humanitarian operations across the country are severely underfunded, forcing agencies to cut food rations and scale back essential health and education services.
“We need urgent support to stabilize this situation,” said a UNAMA spokesperson. “The international community cannot look away while hundreds of thousands of vulnerable families are being pushed over the edge.”
Latest News
Renovation of Afghanistan–Iran border markers to begin in the ‘near future’

Afghanistan’s Minister of Borders and Tribal Affairs, Noorullah Noori, has announced that the long-delayed process of border demarcation and the renovation of markers along the Afghanistan–Iran frontier will officially begin in the near future.
According to a statement from the ministry, Noori made the remarks during a meeting with Ali-Reza Bikdeli, the acting ambassador of Iran in Kabul. Noori assured the Iranian side that the Islamic Emirate is fully committed to speeding up the work and addressing any challenges that may arise during the process.
The Iranian Embassy in Kabul also said that Bikdeli, in the meeting, emphasized that cooperation between the two countries on border issues plays a key role in strengthening and expanding broader bilateral relations.
It is noteworthy that nearly three months ago, officials from both countries agreed to restart the border-marker renovation project, which had remained stalled for seven years. (edited)
Latest News
Afghanistan faces worsening water crisis as millions return home
Around 80% of Kabul’s groundwater is unsafe, and nearly half of the city’s wells have already dried up, the report stated. Experts warn the city’s aquifers could be depleted by 2030.

Afghanistan is confronting a severe water crisis as millions of Afghans return from neighbouring countries, stretching an already fragile water system to its limits.
In an investigation by The Independent, the news outlet found the country has seen weak snowfall this season, with groundwater levels dropping and dams such as the Qargha Dam at risk of running low.
Around 80% of Kabul’s groundwater is unsafe, and nearly half of the city’s wells have already dried up, the report stated. Experts warn the city’s aquifers could be depleted by 2030.
Since 2023, more than five million Afghans have returned from Iran and Pakistan, putting additional pressure on water infrastructure. A Mercy Corps assessment found that three-quarters of households in districts hosting returnees report difficulty accessing clean water.
Prolonged droughts, coupled with aid cuts from countries including the US and UK, have worsened the crisis. Save the Children has reported disruptions to health, education, and clean water services affecting hundreds of thousands. NGOs warn that without significant investment in water infrastructure and improved management, entire neighbourhoods could face displacement.
“The situation is critical but not hopeless,” said Mercy Corps’ Marianna von Zahn. “Afghans are resilient, and communities are already implementing water rationing and exploring water-saving solutions, but urgent support is needed.”
Latest News
Sheikha Al Mayassa unveils Empire of Light: Visions and Voices of Afghanistan
Featuring nearly 150 artefacts, the exhibition brings together archaeological objects, metalwork, glass, manuscripts, textiles, and architectural elements that reflect the country’s rich and diverse cultural legacy.
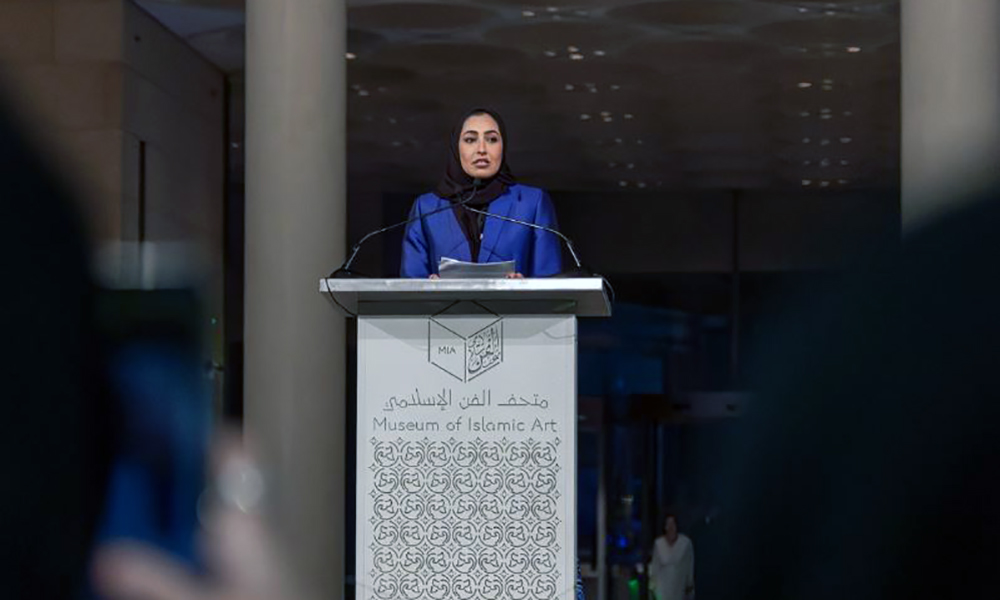

A major exhibition highlighting more than 5,000 years of Afghanistan’s history, culture, and artistic heritage has opened at the Museum of Islamic Art in Doha under the title Empire of Light: Visions and Voices of Afghanistan.
The exhibition was inaugurated by Sheikha Al Mayassa bint Hamad bin Khalifa Al-Thani and will run from February 2 to May 30, 2026. It presents a sweeping narrative of Afghanistan’s past, tracing its role as a crossroads of civilizations, cultures, and ideas from ancient times to the modern era.
Featuring nearly 150 artefacts, the exhibition brings together archaeological objects, metalwork, glass, manuscripts, textiles, and architectural elements that reflect the country’s rich and diverse cultural legacy. The displays explore key historical periods, including the pre-Islamic era, the rise and spread of Islam, and later artistic and cultural developments.
A central theme of the exhibition is heritage preservation. Large-scale wooden architectural models of historic Afghan sites and monuments highlight ongoing conservation and restoration efforts, offering insight into the country’s architectural traditions and craftsmanship.
Organised both thematically and chronologically, Empire of Light aims to challenge narrow perceptions of Afghanistan by presenting its long-standing contributions to global culture, learning, and artistic expression. The exhibition also emphasizes the resilience of Afghan heritage despite decades of conflict and upheaval.
Through immersive displays and carefully curated works, Empire of Light: Visions and Voices of Afghanistan offers visitors a deeper understanding of the country’s historical significance and enduring cultural identity.
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoAfghanistan shine on Day Two of AFC Futsal Asian Cup Indonesia 2026
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoAfghanistan eye second straight win ahead of Malaysia clash at AFC Futsal Asian Cup
-

 Sport1 day ago
Sport1 day agoAFC Futsal Asian Cup: Afghanistan to face Iran in crucial Group D clash
-

 Sport3 days ago
Sport3 days agoAfghanistan dominates Malaysia 7–0 in AFC Futsal Asian Cup
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoAustralia announces $50 million in new humanitarian aid for Afghanistan
-

 Sport2 days ago
Sport2 days agoT20 World Cup 2026: Afghanistan national cricket team arrives in India
-

 Business2 days ago
Business2 days agoPakistan, China plan to extend CPEC to Afghanistan, revive trilateral framework
-
 Health4 days ago
Health4 days agoPakistan becomes latest Asian country to introduce checks for deadly Nipah virus

























