Business
World Bank warns of increased poverty due to COVID-19 shock

The World Bank has stated that a clear commitment from international partners to continue grant support would help reduce uncertainty and improve investor confidence in Afghanistan which would in turn enable the country to recover from the severe impacts of the COVID-19 crisis.
In its twice-yearly report, the World Bank stated that South Asia as a whole is set to plunge into its worst-ever recession due to the pandemic which will take a heavy toll on informal workers and push millions of people in the region into extreme poverty.
According to the report, although Afghanistan experienced moderate growth in 2019 as the agricultural sector recovered from the impacts of drought, the economy is estimated to have contracted sharply in the first half of 2020 due to economic disruptions associated with nation-wide lockdowns, border closures, and declining remittance inflows.
In addition, the report stated that medium-term prospects are subject to high levels of uncertainty, related to the COVID-19 pandemic, peace talks and future international security and aid support.
“Given the shock to the economy, poverty is expected to increase in 2020,” the report stated.
While there was significant growth in wheat production, the World Bank said this was not enough to offset the large negative impact of COVID-19 on other sectors of the economy.
The World Bank stated that while inflation was low in 2019 (averaging 2.3 percent) it increased significantly in 2020.
One reason was that in March and April 2020 – during lockdown – panic buying and import disruptions resulted in a sharp increase in food prices, which led government to adopt administrative measures to prevent price gouging.
Government also initiated an emergency wheat distribution program that resulted in a food inflation decline in the months that followed.
In the first quarter of 2020 Afghanistan registered a growth in exports of 11 percent year-on-year, which reflected the improved performance of air corridors. However, a weak domestic demand led to a 14 percent decline in imports.
“In the second quarter of 2020, both imports and exports fell precipitously given border closures and disruptions to trade and transportation, with greater absolute declines in imports driving an improvement in the trade and current account balances,” the report read.
With the onset of the COVID-19 crisis, weak economic activity, disruptions to trade and compliance, revenue performance deteriorated significantly and revenue estimates for 2020 were revised downward by over 30 percent (from Afs 209 billion to 144 billion) in the budget mid-year review.
“Total domestic revenue collection at end-June reached Afs 74.7 billion, 20 percent lower than the initial budget target,” the report stated.
Poverty meanwhile is believed to have worsened in 2019 surpassing 54.5 percent amid continued violence and political uncertainty and “in the first half of 2020, with declining household incomes due to economic hardship, higher food prices due to COVID-19, a significant fall in remittances, and high returnee flows, poverty is estimated to have further increased,” the report read.
According to the report, the outlook for the rest of 2020 was grim as the GDP is expected to contract by 5.5 percent – again largely due to the impact of the pandemic.
“In following years, the pace of recovery is expected to be constrained in a context of continued insecurity, uncertainties regarding the outcome of planned peace talks, and questions about the level and duration of international security and aid support.
“The trade deficit is projected to narrow to 26 percent of GDP down from 30.4 percent in 2019. While exports are projected to fall by 24 percent, imports are expected to decline by around 18 percent,” read the report.
World Bank analysis meanwhile suggests that the combination of reduced incomes and higher prices could drive the poverty rate to as high as 72 percent in the medium term.
“Over the medium term, the poverty outlook hinges on the pace of economic recovery and the continued provision of international aid and humanitarian support,” the report read.
“The main source of downside risk to the outlook stems from possible further adverse COVID-19 developments,” the World Bank stated adding that additional sources of risk include further political instability, a deterioration of security conditions, uncertainties associated with the planned peace agreement with the Taliban, and precipitous reductions in aid flow.
“By contrast, on the upside, a sustainable and credible political settlement with the Taliban could help boost growth, confidence and private investment,” the bank stated.
In terms of recommendations, the World Bank stated that given Afghanistan’s declining revenues and constrained fiscal potential, public expenditures need to be carefully directed to protecting the vulnerable, limiting long-term economic damage, and establishing solid foundations for economic recovery.
“To support households, the government should prioritize: i) targeted social protection measures; and ii) ensuring the continued provision of basic services, especially healthcare.
“To support the private sector, priorities include: i) pursuing business regulatory reforms to facilitate new investment; ii) expanding access to credit; iii) ensuring the continued provision of basic infrastructure; and iv) avoiding accumulating arrears to private sector vendors.”
Business
Uzbekistan approves feasibility study agreement for Trans-Afghan Railway
The agreement builds on a tripartite document signed on July 17, 2025, which outlined cooperation on preparing a feasibility study for the Termez–Kharlachi railway corridor.
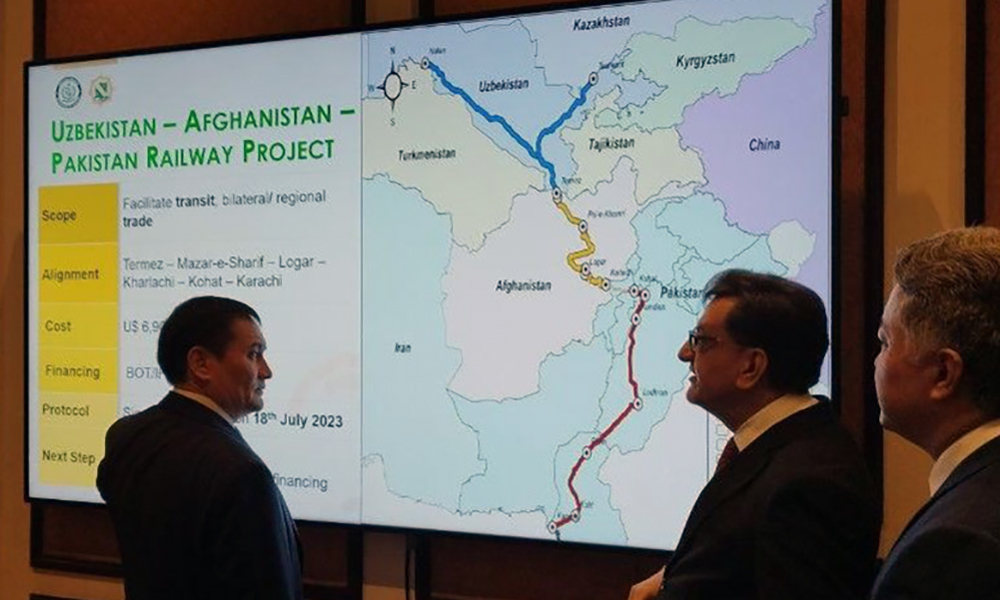
Uzbekistan has ratified an international agreement to prepare a feasibility study for the Naybabad–Kharlachi section of the Trans-Afghan Railway, formalizing its participation in the project.
President Shavkat Mirziyoyev signed a decree on February 4 approving the agreement.
The framework agreement involves the transport ministries of Uzbekistan, Afghanistan and Pakistan and provides for joint work on a feasibility study for the proposed railway line between Naybabad and Kharlachi. The section forms part of the wider Trans-Afghan Railway project aimed at strengthening transport links between Central and South Asia.
Under the decree, Uzbekistan’s Ministry of Transport has been designated as the competent authority responsible for implementing the agreement. The Ministry of Foreign Affairs has been tasked with notifying Kabul and Islamabad that Uzbekistan has completed the internal procedures required for the agreement to enter into force.
The agreement builds on a tripartite document signed on July 17, 2025, which outlined cooperation on preparing a feasibility study for the Termez–Kharlachi railway corridor.
The planned route is expected to run through Termez, Naybabad, Maidanshahr, Logar and Kharlachi, providing a transit corridor through Afghanistan.
The feasibility study will be commissioned by the Tripartite Project Office for the Development Strategy of International Transport Corridors under Uzbekistan Railways.
Established in Tashkent in May 2023, the office also operates branches in Kabul and Islamabad to coordinate the project.
First proposed in 2018, the Trans-Afghan Railway was initially projected to carry up to 20 million tons of cargo annually at a cost of about $5 billion. Cost estimates have since been revised.
In July 2022, Uzbekistan Railways cited an estimate of $4.6 billion with a construction period of up to five years, while Pakistan’s Ministry of Railways put the cost at $8.2 billion in December 2024.
More recent assessments have placed the overall cost at around $7 billion, with a public-private partnership under a Build-Operate-Transfer model among the options under consideration.
Business
Afghanistan seeks expanded ties with Russia in energy, mining and infrastructure
TASS reported that Kabul is also prepared to cooperate with Moscow in the extraction of mineral resources.

Afghanistan has expressed strong interest in broadening trade and economic cooperation with Russia, with a particular focus on energy, mining and infrastructure projects, according to Russia’s TASS news agency.
In an interview with TASS, Afghanistan’s Ambassador to Moscow, Gul Hassan, said Kabul is keen to import oil and gas from Russia as part of efforts to deepen bilateral economic ties.
He noted that trade relations between the two countries are progressing and that, if key obstacles—especially banking restrictions—are addressed, Afghanistan could also import medicines, industrial goods, grain, vegetable oils and other commodities from Russia.
In return, the ambassador said Afghanistan is ready to export fresh and dried fruits, vegetables, medicinal plants, carpets and mineral resources to the Russian market, adding that expanding export-import operations could significantly increase bilateral trade volumes.
He also revealed plans to open an exhibition of Afghan products in Moscow, which he said would help boost trade turnover.
TASS reported that Kabul is also prepared to cooperate with Moscow in the extraction of mineral resources.
Hassan described the economy as a central pillar of Afghanistan’s foreign policy, emphasizing the government’s goal of positioning the country as a key link in regional economic integration and attracting foreign investment.
He noted that Russian companies have long shown interest in Afghanistan’s industrial, mining and infrastructure sectors.
The ambassador further told TASS that Russian firms are already in talks with relevant Afghan authorities on the construction of small hydroelectric power plants.
Representatives of several Russian companies have reportedly visited Afghanistan and held meetings with officials and technical experts.
According to Hassan, practical steps toward cooperation in the energy and power generation sectors are expected in the near future, pointing to a potential new phase in Afghan-Russian economic relations.
Business
Pakistan, China plan to extend CPEC to Afghanistan, revive trilateral framework
The proposed CPEC expansion into Afghanistan is seen as a move to enhance regional economic integration amid shifting geopolitical dynamics.

Pakistan and China are moving forward with plans to extend the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) into Afghanistan, a strategic step aimed at bolstering regional connectivity and economic cooperation. The expansion, along with the revival of the Pakistan-China-Afghanistan trilateral framework, was discussed in a recent briefing to the Pakistani Senate Standing Committee on Foreign Affairs.
According to Pakistan Today, officials from Pakistan’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs outlined the details during a session in Islamabad, where they reviewed key aspects of Pakistan’s foreign relations, regional developments, and economic diplomacy.
Officials emphasized that Pakistan’s relationship with China remains strong, underscoring the “all-weather” strategic partnership between the two nations. Strengthening ties with Beijing, they stated, continues to be a cornerstone of Pakistan’s foreign policy. This includes unwavering support for China’s position on regional and international issues, particularly the One-China policy and matters related to territorial integrity.
The briefing also touched upon China’s consistent backing of Pakistan in various areas, including sovereignty, economic stability, counter-terrorism, and support for Pakistan’s exit from the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) grey list.
The Kashmir issue was also addressed, with officials noting that China considers it an unresolved matter and advocates for a peaceful resolution in line with UN Security Council resolutions.
The proposed CPEC expansion into Afghanistan is seen as a move to enhance regional economic integration amid shifting geopolitical dynamics. Officials stated that reviving the trilateral framework is part of broader efforts to foster greater cooperation and connectivity in the region, with an eye on long-term stability and prosperity.
The move also reflects both countries’ desire to further integrate Afghanistan into the regional economic landscape, a key element in fostering peace and development.
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoAfghanistan to grant one- to ten-year residency to foreign investors
-

 Sport5 days ago
Sport5 days agoIndonesia shock Japan to reach historic AFC Futsal Asian Cup final
-

 Sport3 days ago
Sport3 days agoIran clinch AFC Futsal Asian Cup 2026 in penalty shootout thriller
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoAfghanistan says Pakistan is shifting blame for its own security failures
-

 International Sports2 days ago
International Sports2 days agoWinter Olympics gain momentum as medal table takes shape
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoTraffic police receive new cars
-

 Regional4 days ago
Regional4 days agoIran’s FM calls Oman-mediated talks with US ‘good start’
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoTajik foreign minister urges international community to help Afghanistan address its challenges
























