Health
Pig heart transplanted into human patient for the second time
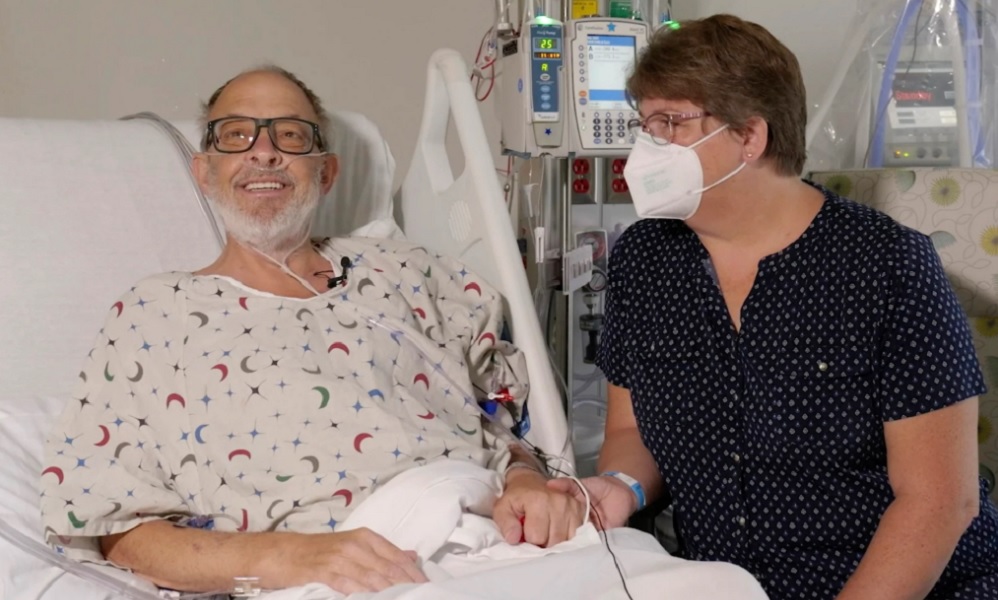
Surgeons have transplanted a pig’s heart into a dying man in a bid to prolong his life – only the second patient to ever undergo such an experimental feat. Two days later, the man was cracking jokes and able to sit in a chair, Maryland doctors said Friday.
The 58-year-old Navy veteran was facing near-certain death from heart failure but other health problems meant he wasn’t eligible for a traditional heart transplant, according to doctors at University of Maryland Medicine, the Associated Press reported.
“Nobody knows from this point forward. At least now I have hope and I have a chance,” Lawrence Faucette, from Frederick, Maryland, said in a video recorded by the hospital before Wednesday’s operation. “I will fight tooth and nail for every breath I can take.”
While the next few weeks will be critical, doctors were thrilled at Faucette’s early response to the pig organ.
“You know, I just keep shaking my head – how am I talking to someone who has a pig heart?” Dr. Bartley Griffith, who performed the transplant, told The Associated Press. He said doctors are feeling “a great privilege but, you know, a lot of pressure.”
The same Maryland team last year performed the world’s first transplanet of a genetically modified pig heart into another dying man, David Bennett, who survived just two months.
There’s a huge shortage of human organs donated for transplant. Last year, there were just over 4,100 heart transplants in the U.S., a record number but the supply is so tight that only patients with the best chance of long-term survival get offered one.
Attempts at animal-to-human organ transplants have failed for decades, as people’s immune systems immediately destroyed the foreign tissue. Now scientists are trying again using pigs genetically modified to make their organs more humanlike.
Recently, scientists at other hospitals have tested pig kidneys and hearts in donated human bodies, hoping to learn enough to begin formal studies of what are called xenotransplants.
To make this new attempt in a living patient outside of a rigorous trial, the Maryland researchers required special permission from the Food and Drug Administration, under a process reserved for certain emergency cases with no other options.
It took over 300 pages of documents filed with FDA, but the Maryland researchers made their case that they’d learned enough from their first attempt last year – even though that patient died for reasons that aren’t fully understood – that it made sense to try again.
And Faucette, who retired as a lab technician at the National Institutes of Health, had to agree that he understood the procedure’s risks.
In a statement his wife, Ann Faucette, said: “We have no expectations other than hoping for more time together. That could be as simple as sitting on the front porch and having coffee together.”
What’s different this time: Only after last year’s transplant did scientists discover signs of a pig virus lurking inside the heart – and they now have better tests to look for hidden viruses. They also made some medication changes.
Possibly more important, while Faucette has end-stage heart failure and was out of other options, he wasn’t as near death as the prior patient.
By Friday, his new heart was functioning well without any supportive machinery, the hospital said.
“It’s just an amazing feeling to see this pig heart work in a human,” said Dr. Muhammad Mohiuddin, the Maryland team’s xenotransplantation expert. But, he cautioned, “we don’t want to predict anything. We will take every day as a victory and move forward.”
This kind of single-patient “compassionate use” can provide some information about how the pig organ works but not nearly as much as more formal testing, said Karen Maschke, a research scholar at the Hastings Center who is helping develop ethics and policy recommendations for xenotransplant clinical trials. That FDA allowed this second case “suggests that the agency is not ready to permit a pig heart clinical trial to start,” Mashke added.
The pig heart, provided by Blacksburg, Virginia-based Revivicor, has 10 genetic modifications – knocking out some pig genes and adding some human ones to make it more acceptable to the human immune system.
Health
Afghanistan opens first national cancer diagnosis and treatment hospital
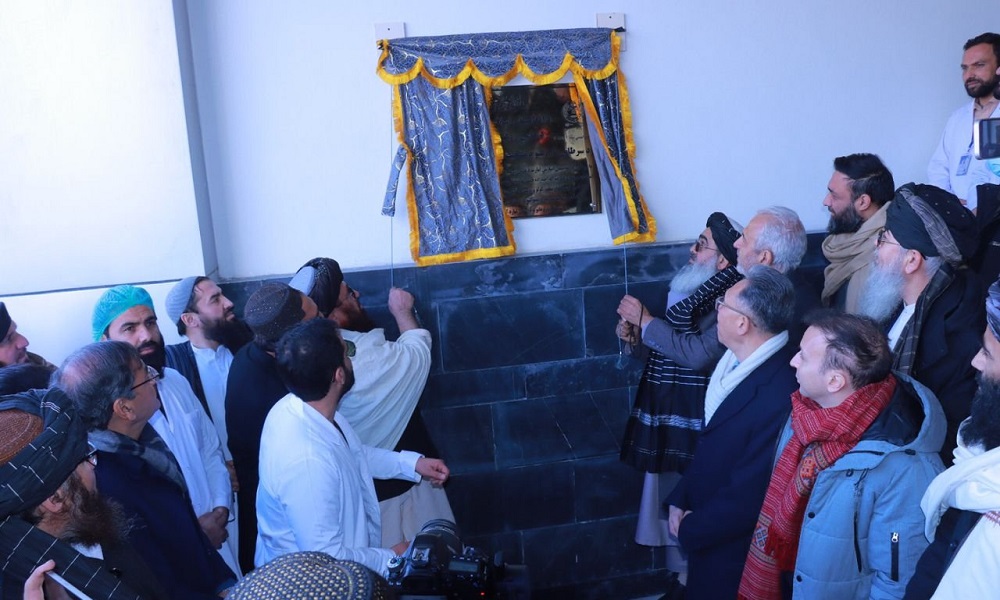

The Ministry of Public Health announced on Thursday that Afghanistan has inaugurated its first national hospital dedicated to the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, marking a major step forward in the country’s healthcare services.
The facility, named the National Cancer Diagnostic and Therapeutic Hospital, has officially begun operations and will provide specialized care for cancer patients across the country.
Speaking at the inauguration ceremony, Public Health Minister Noor Jalal Jalali said the 200-bed hospital aims to offer hope and improved treatment options for patients suffering from cancer.
“Fortunately, we are jointly opening a 200-bed hospital for cancer patients, and we hope that this hospital will become a source of hope and healing for those in need,” Jalali said.
The minister added that specialized training programs will soon be launched at the hospital to educate and train domestic medical specialists. He noted that reforms have already been implemented to improve facilities and ensure better healthcare services.
Jalali also emphasized international cooperation in the project, saying that radiotherapy services will be introduced at the hospital with support from India. According to the ministry, India has so far provided $1 million in assistance, including 10 tons of medicines and medical equipment, to support cancer treatment in Afghanistan.
The opening of the hospital is expected to reduce the need for Afghan patients to seek costly cancer treatment abroad and improve access to specialized care inside the country.
Health
Pakistan becomes latest Asian country to introduce checks for deadly Nipah virus
Authorities in Pakistan have ordered enhanced screening of people entering the country for signs of infections of the deadly Nipah virus after India confirmed two cases, adding to the number of Asian countries stepping up controls.
Thailand, Singapore, Hong Kong, Malaysia, Indonesia and Vietnam have also tightened screening at airports, Reuters reported.
The Nipah virus can cause fever and brain inflammation and has a high mortality rate. There is also no vaccine. But transmission from person to person is not easy and typically requires prolonged contact with an infected individual.
“It has become imperative to strengthen preventative and surveillance measures at Pakistan’s borders,” the Border Health Services department said in a statement.
“All travelers shall undergo thermal screening and clinical assessment at the Point of Entry,” which includes seaports, land borders and airports, the department added.
The agency said travellers would need to provide transit history for the preceding 21-day period to check whether they had been through “Nipah-affected or high-risk regions”.
There are no direct flights between Pakistan and India and travel between the two countries is extremely limited, particularly since their worst fighting in decades in May last year.
In Hanoi, the Vietnamese capital’s health department on Wednesday also ordered the screening of incoming passengers at Noi Bai airport, particularly those arriving from India and the eastern state of West Bengal, where the two health workers were confirmed to have the virus in late December.
Passengers will be checked with body temperature scanners to detect suspected cases. “This allows for timely isolation, epidemiological investigation,” the department said in a statement.
That follows measures by authorities in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam’s largest city, who said they had tightened health controls at international border crossings.
India’s health ministry said this week that authorities have identified and traced 196 contacts linked to the two cases with none showing symptoms and all testing negative for the virus.
Nipah is a rare viral infection that spreads largely from infected animals, mainly fruit bats, to humans. It can be asymptomatic but it is often very dangerous, with a case fatality rate of 40% to 75%, depending on the local healthcare system’s capacity for detection and management, according to the World Health Organization.
The virus was first identified just over 25 years ago during an outbreak among pig farmers in Malaysia and Singapore, although scientists believe it has circulated in flying foxes, or fruit bats, for thousands of years.
The WHO classifies Nipah as a priority pathogen. India regularly reports sporadic infections, particularly in the southern state of Kerala, regarded as one of the world’s highest-risk regions for Nipah.
As of December 2025, there have been 750 confirmed Nipah infections globally, with 415 deaths, according to the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations, which is funding a vaccine trial to help stop Nipah.
Health
Afghan deputy health minister urges increased international support for health sector
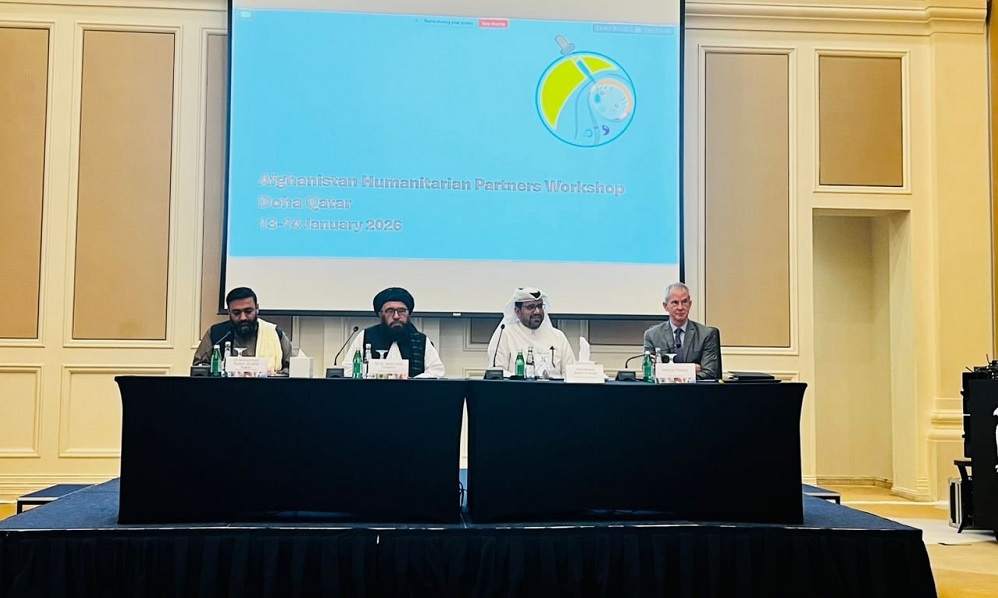

Abdul Wali Haqqani, Afghanistan’s Deputy Public Health Minister for Health Services, has called for increased international assistance to strengthen the country’s health sector, stressing the need for sustained and growing financial support.
Speaking at the an international conference in Qatar, Haqqani highlighted critical needs in vaccination programs, primary healthcare, maternal and child health, and preparedness for emergency and epidemic diseases.
He emphasized that aligning international health assistance with Afghanistan’s national health policy would not only improve service quality but also ensure more effective and transparent management of resources.
The deputy minister added that the Ministry of Public Health views such global forums as vital for enhancing cooperation, building trust, and delivering equitable and sustainable healthcare services to the Afghan population.
-

 Sport5 days ago
Sport5 days agoAFC Futsal Asian Cup 2026: Final eight confirmed
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoJapan trumps Afghanistan 6-0 in AFC Futsal Asian Cup quarter-final
-

 Sport5 days ago
Sport5 days agoAfghanistan in new kit for T20 World Cup warm-up against Scotland
-

 Sport3 days ago
Sport3 days agoHosts and heavyweights advance as AFC Futsal Asian Cup reaches semifinals
-

 International Sports5 days ago
International Sports5 days agoPakistan to boycott T20 World Cup group match against India
-

 Sport5 days ago
Sport5 days agoAfghanistan crush Scotland in ICC T20 World Cup warm-up
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoTerrorist threat in Afghanistan must be taken seriously, China tells UNSC
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoUzbekistan, Pakistan advance Trans-Afghan railway project
























