Health
Dengue will ‘take off’ in southern Europe, US, Africa this decade, WHO scientist says

Dengue fever will become a major threat in the southern United States, southern Europe and new parts of Africa this decade, the WHO’s chief scientist said, as warmer temperatures create the conditions for the mosquitoes carrying the infection to spread.
The illness has long been a scourge in much of Asia and Latin America, causing an estimated 20,000 deaths each year. Rates of the disease have already risen eight-fold globally since 2000, driven largely by climate change as well as the increased movement of people and urbanization, Reuters reported.
Many cases go unrecorded, but in 2022 4.2 million cases were reported worldwide and public health officials have warned that near-record levels of transmission are expected this year. Bangladesh is currently experiencing its worst-ever outbreak, with more than 1,000 deaths.
“We need to talk much more proactively about dengue,” Jeremy Farrar, an infectious diseases specialist who joined the World Health Organization in May this year, told Reuters.
“We need to really prepare countries for how they will deal with the additional pressure that will come… in the future in many, many big cities.”
Farrar previously spent 18 years working in Vietnam on tropical diseases including dengue. He later headed up the Wellcome Trust global health charity and advised the UK government on its COVID-19 response before joining the WHO in May this year.
Farrar said the infection is likely to “take off” and become endemic in parts of the United States, Europe and Africa – all regions where there has already been some limited local transmission – as global warming makes new areas hospitable to the mosquitoes that spread it. That will put acute pressure on hospital systems in many countries, he warned.
“The clinical care is really intensive, it requires a high ratio of nurses to patients,” he said. “I really worry when this becomes a big issue in sub-Saharan Africa.”
Most people who get dengue do not have symptoms, meaning case rates are thought to be far higher than the reported numbers. Those who do can experience fever, muscle spasms and joint pain so severe it is known as “break-bone fever.” In severe cases – less than 1% – it can be fatal.
There is no specific treatment for dengue, although there is a vaccine available. Earlier this week, the WHO recommended Takeda Pharmaceuticals’ Qdenga vaccine for children aged 6 to 16 in areas where the infection is a significant public health problem.
Qdenga is also approved by the EU regulator, but Takeda withdrew its application in the United States earlier this year, citing data collection issues. Takeda said it was still in talks with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration about the vaccine.
Preparing new regions of the world to deal with dengue means ensuring that any public health funds get spent in the right areas, Farrar said, including on the best way to control the mosquito.
Dengue is spread by infected Aedes aegypti mosquitoes, which behave differently to the malaria-carrying kind. For example, they bite people indoors, and they bite all day rather than overnight. They also breed in very shallow water.
Farrar said proper prevention would include triaging plans for hospitals as well as scientific innovation alongside other key factors, such as urban planning, to avoid areas of standing water near or in houses.
“We need to combine different sectors that are not used to working together,” he said.
Health
Afghan delegation heads to Turkey for medicine talks

Naemullah Ayoubi, Director General of Drug and Health Products Regulation at Afghanistan’s Ministry of Public Health, has departed for Turkey on an official visit accompanied by a technical delegation.
The Ministry of Public Health said the delegation will hold meetings with officials from Turkey’s pharmaceutical regulatory authority and discuss a number of key issues related to the regulation of medicines and health products.
The delegation is also scheduled to visit several pharmaceutical manufacturing factories in Turkey.
According to the ministry, the visit aims to strengthen coordination between the two countries in the production and import of medicines, in order to ensure the availability of high-quality and affordable pharmaceuticals for people in Afghanistan in both the short and long term.
Health
Afghanistan opens first national cancer diagnosis and treatment hospital
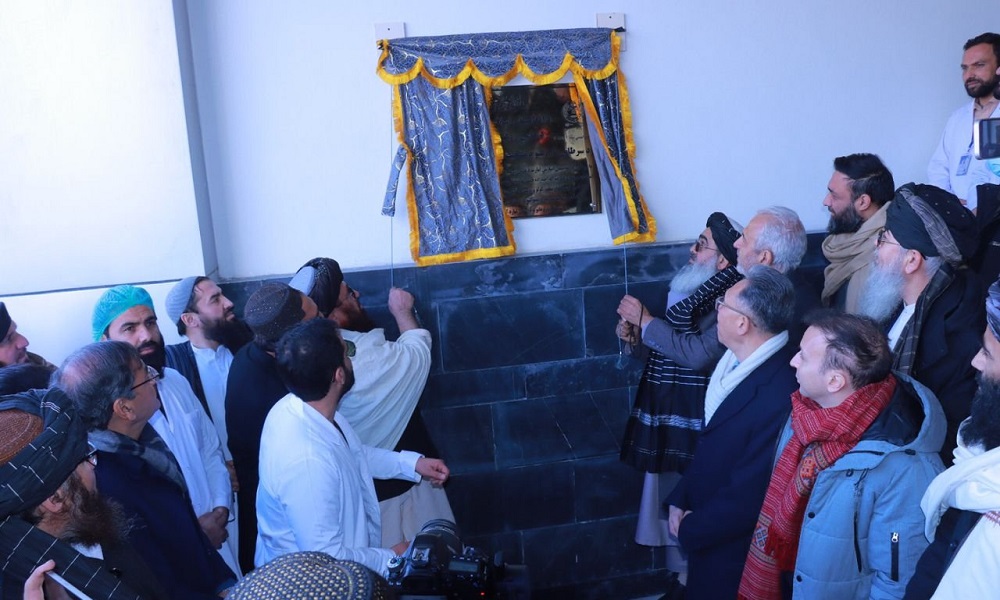

The Ministry of Public Health announced on Thursday that Afghanistan has inaugurated its first national hospital dedicated to the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, marking a major step forward in the country’s healthcare services.
The facility, named the National Cancer Diagnostic and Therapeutic Hospital, has officially begun operations and will provide specialized care for cancer patients across the country.
Speaking at the inauguration ceremony, Public Health Minister Noor Jalal Jalali said the 200-bed hospital aims to offer hope and improved treatment options for patients suffering from cancer.
“Fortunately, we are jointly opening a 200-bed hospital for cancer patients, and we hope that this hospital will become a source of hope and healing for those in need,” Jalali said.
The minister added that specialized training programs will soon be launched at the hospital to educate and train domestic medical specialists. He noted that reforms have already been implemented to improve facilities and ensure better healthcare services.
Jalali also emphasized international cooperation in the project, saying that radiotherapy services will be introduced at the hospital with support from India. According to the ministry, India has so far provided $1 million in assistance, including 10 tons of medicines and medical equipment, to support cancer treatment in Afghanistan.
The opening of the hospital is expected to reduce the need for Afghan patients to seek costly cancer treatment abroad and improve access to specialized care inside the country.
Health
Pakistan becomes latest Asian country to introduce checks for deadly Nipah virus
Authorities in Pakistan have ordered enhanced screening of people entering the country for signs of infections of the deadly Nipah virus after India confirmed two cases, adding to the number of Asian countries stepping up controls.
Thailand, Singapore, Hong Kong, Malaysia, Indonesia and Vietnam have also tightened screening at airports, Reuters reported.
The Nipah virus can cause fever and brain inflammation and has a high mortality rate. There is also no vaccine. But transmission from person to person is not easy and typically requires prolonged contact with an infected individual.
“It has become imperative to strengthen preventative and surveillance measures at Pakistan’s borders,” the Border Health Services department said in a statement.
“All travelers shall undergo thermal screening and clinical assessment at the Point of Entry,” which includes seaports, land borders and airports, the department added.
The agency said travellers would need to provide transit history for the preceding 21-day period to check whether they had been through “Nipah-affected or high-risk regions”.
There are no direct flights between Pakistan and India and travel between the two countries is extremely limited, particularly since their worst fighting in decades in May last year.
In Hanoi, the Vietnamese capital’s health department on Wednesday also ordered the screening of incoming passengers at Noi Bai airport, particularly those arriving from India and the eastern state of West Bengal, where the two health workers were confirmed to have the virus in late December.
Passengers will be checked with body temperature scanners to detect suspected cases. “This allows for timely isolation, epidemiological investigation,” the department said in a statement.
That follows measures by authorities in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam’s largest city, who said they had tightened health controls at international border crossings.
India’s health ministry said this week that authorities have identified and traced 196 contacts linked to the two cases with none showing symptoms and all testing negative for the virus.
Nipah is a rare viral infection that spreads largely from infected animals, mainly fruit bats, to humans. It can be asymptomatic but it is often very dangerous, with a case fatality rate of 40% to 75%, depending on the local healthcare system’s capacity for detection and management, according to the World Health Organization.
The virus was first identified just over 25 years ago during an outbreak among pig farmers in Malaysia and Singapore, although scientists believe it has circulated in flying foxes, or fruit bats, for thousands of years.
The WHO classifies Nipah as a priority pathogen. India regularly reports sporadic infections, particularly in the southern state of Kerala, regarded as one of the world’s highest-risk regions for Nipah.
As of December 2025, there have been 750 confirmed Nipah infections globally, with 415 deaths, according to the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations, which is funding a vaccine trial to help stop Nipah.
-

 Latest News2 days ago
Latest News2 days agoAfghanistan to grant one- to ten-year residency to foreign investors
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoTerrorist threat in Afghanistan must be taken seriously, China tells UNSC
-

 Sport5 days ago
Sport5 days agoAfghanistan beat West Indies in final T20 WC warm-up match
-

 Sport3 days ago
Sport3 days agoIndonesia shock Japan to reach historic AFC Futsal Asian Cup final
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoMilano Cortina 2026 Winter Olympics: What You Need to Know
-

 Sport2 days ago
Sport2 days agoIran clinch AFC Futsal Asian Cup 2026 in penalty shootout thriller
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoUS Justice Department to seek death penalty for Afghan suspect in National Guard shooting
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoUzbekistan, Kazakhstan discuss cooperation on Afghanistan
























