Science & Technology
NASA rover finds potential sign of ancient life in Martian rocks
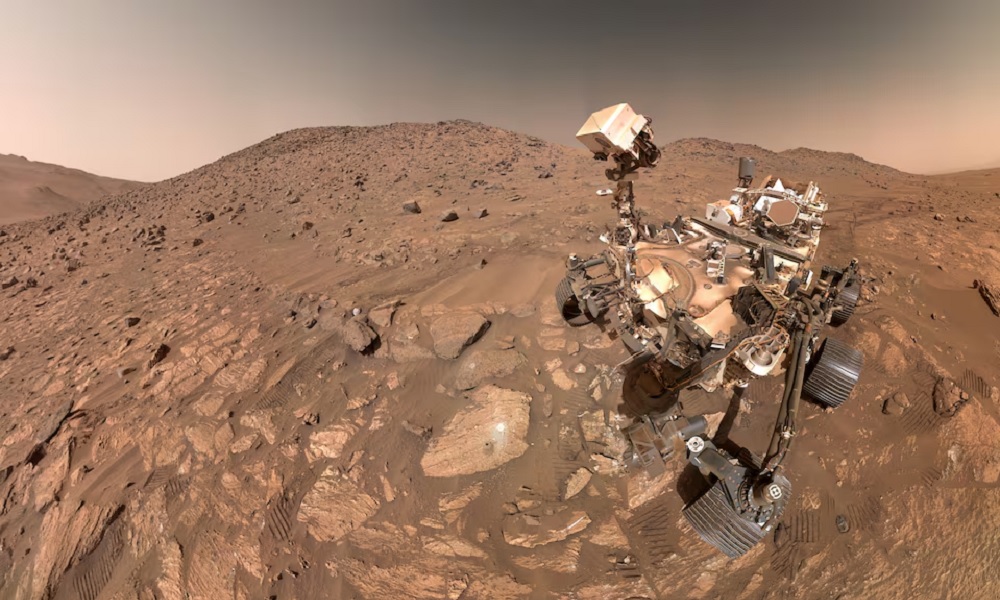

A sample obtained by NASA’s Perseverance rover of reddish rock formed billions of years ago from sediment on the bottom of a lake contains potential signs of ancient microbial life on Mars, according to scientists, though the minerals spotted in the sample also can form through nonbiological processes.
The discovery by the six-wheeled rover in Jezero Crater represents one of the best pieces of evidence to date about the possibility that Earth’s planetary neighbor once harbored life, Reuters reported.
Perseverance scientist Joel Hurowitz of Stony Brook University, lead author of the study published in the journal Nature, said a “potential biosignature” was detected in rock that formed at a time when Jezero Crater was believed to have been a watery environment, between 3.2 and 3.8 billion years ago.
Acting NASA Administrator Sean Duffy told a news conference that the U.S. space agency’s scientists examined the data for a year and concluded that “we can’t find another explanation, so this very well could be the clearest sign of life that we’ve ever found on Mars – which is incredibly exciting.”
NASA released an image of the rock – a very fine-grained, rusty-red mudstone – bearing ring-shaped features resembling leopard spots and dark marks resembling poppy seeds. Those features may have been produced when the rock was forming by chemical reactions involving microbes, according to the researchers.
A potential biosignature is defined as a substance or structure that may have a biological origin but needs more data or further study before a conclusion can be made about the absence or presence of life.
Nicky Fox, associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, noted that the scientists were not announcing the discovery of a living organism.
“It’s not life itself,” Fox told the news conference.
The rover since 2021 has been exploring Jezero Crater, an area in the planet’s northern hemisphere that once was flooded with water and home to an ancient lake basin. Scientists believe river channels spilled over the crater wall and created a lake.
Perseverance has been analyzing rocks and loose material called regolith with its onboard instruments and then collecting samples and sealing them in tubes stored inside the rover.
It collected the sample named Sapphire Canyon in July 2024 from a rock called Cheyava Falls in a locale known as Bright Angel rock formation. The sample came from a set of rocky outcrops on the edges of Neretva Vallis, an ancient river valley about a quarter of a mile (400 meters) wide carved by water rushing into the crater.
TELLTALE MINERALS
Two minerals were detected that appear to have formed as a result of chemical reactions between the mud of the Bright Angel formation and organic matter present in that mud, Hurowitz said. They are: vivianite, a mineral bearing iron and phosphorus, and greigite, a mineral bearing iron and sulfur.
“These reactions appear to have taken place shortly after the mud was deposited on the lake bottom. On Earth, reactions like these, which combine organic matter and chemical compounds in mud to form new minerals like vivianite and greigite, are often driven by the activity of microbes,” Hurowitz told Reuters.
“The microbes are consuming the organic matter in these settings and producing these new minerals as a byproduct of their metabolism,” Hurowitz said.
The rover’s instruments found that the rock was rich in organic carbon, sulfur, phosphorus and iron in its oxidized form, rust. This combination of chemical compounds could have offered a rich source of energy for microbial metabolisms, Hurowitz said.
But Hurowitz offered some words of caution.
“The reason, however, that we cannot claim this is more than a potential biosignature is that there are chemical processes that can cause similar reactions in the absence of biology, and we cannot rule those processes out completely on the basis of rover data alone,” Hurowitz said.
Mars has not always been the inhospitable place it is today, with liquid water on its surface in the distant past.
The sample collected and analyzed by Perseverance provides a new example of a type of potential biosignature that the research community can explore to try to understand whether or not these features were formed by life, Hurowitz said, “or alternatively, whether nature has conspired to present features that mimic the activity of life.”
“We can make a lot of progress on this question with laboratory experiments and fieldwork here on Earth to try to understand the various pathways that might create features like the ones we observe in the Bright Angel formation. But the ultimate tests can only be performed on the Sapphire Canyon core sample if and when it is brought back to Earth for study,” Hurowitz added.
U.S. President Donald Trump’s current budget proposal would cancel NASA’s existing Mars Sample Return mission. Duffy said NASA is examining various ways for potential sample retrieval or even sending equipment to Mars to do further analysis there.
“We’re going to look at our budgets and we’re going to look at our timing, and how we spend money better and what technology do we have to get samples back more quickly,” Duffy said.
Science & Technology
Australia social media ban set to take effect, sparking a global crackdown
For the social media businesses, the implementation marks a new era of structural stagnation as user numbers flatline and time spent on platforms shrinks, studies show.

Australia is set to become the first country to implement a minimum age for social media use on Wednesday, with platforms like Instagram, TikTok and YouTube forced to block more than a million accounts, marking the beginning of an expected global wave of regulation.
From midnight, 10 of the biggest platforms will be required to block Australians aged under 16 or be fined up to A$49.5 million ($33 million), Reuters reported.
The law received harsh criticism from major technology companies and free speech advocates, but was praised by parents and child advocates.
The rollout closes out a year of speculation about whether a country can block children from using technology that is built into modern life. And it begins a live experiment that will be studied globally by lawmakers who want to intervene directly because they are frustrated by what they say is a tech industry that has been too slow to implement effective harm-minimisation efforts.
Governments from Denmark to Malaysia – and even some states in the U.S., where platforms are rolling back trust and safety features – say they plan similar steps, four years after a leak of internal Meta (META.O) documents showed the company knew its products contributed to body image problems and suicidal thoughts among teenagers while publicly denying the link existed.
“While Australia is the first to adopt such restrictions, it is unlikely to be the last,” said Tama Leaver, a professor of internet studies at Curtin University.
“Governments around the world are watching how the power of Big Tech was successfully taken on. The social media ban in Australia … is very much the canary in the coal mine.”
A spokesperson for the British government, which in July began forcing websites hosting pornographic content to block under-18 users, said it was “closely monitoring Australia’s approach to age restrictions.”
“When it comes to children’s safety, nothing is off the table,” they added.
Few will scrutinise the impact as closely as the Australians. The eSafety Commissioner, an Australian regulator tasked with enforcing the ban, hired Stanford University and 11 academics to analyse data on thousands of young Australians covered by the ban for at least two years.
Though the ban covers 10 platforms initially, including Alphabet’s (GOOGL.O), YouTube, Meta’s Instagram and TikTok, the government has said the list will change as new products appear and young users switch to alternatives.
Of the initial 10, all but Elon Musk’s X have said they will comply using age inference – guessing a person’s age from their online activity – or age estimation, which is usually based on a selfie. They might also check with uploaded identification documents or linked bank account details.
Musk has said the ban “seems like a backdoor way to control access to the internet by all Australians” and most platforms have complained that it violates people’s right to free speech.
For the social media businesses, the implementation marks a new era of structural stagnation as user numbers flatline and time spent on platforms shrinks, studies show.
Platforms say they don’t make much money showing advertisements to under-16s, but they add that the ban interrupts a pipeline of future users. Just before the ban took effect, 86% of Australians aged 8 to 15 used social media, the government said.
“The days of social media being seen as a platform for unbridled self-expression, I think, are coming to an end,” said Terry Flew, the co-director of University of Sydney’s Centre for AI, Trust and Governance.
Platforms responded to negative headlines and regulatory threats with measures like a minimum age of 13 and extra privacy features for teenagers, but “if that had been the structure of social media in the boom period, I don’t think we’d be having this debate,” he added.
Science & Technology
Ethiopian volcano erupts for first time in nearly 12,000 years
Ash from the eruption drifted across the region, spreading over Yemen, Oman, India, and parts of Pakistan.
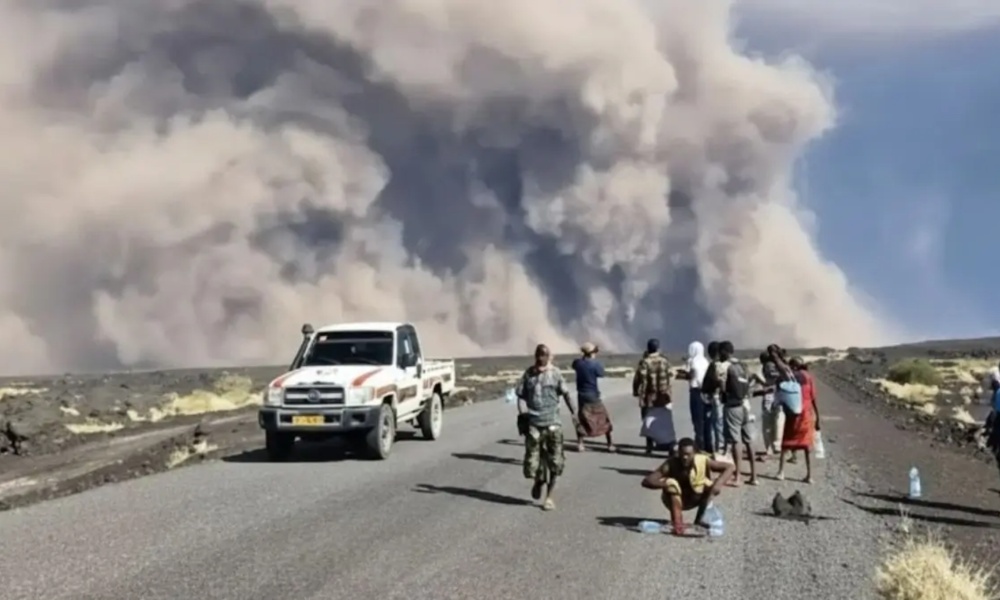

The Hayli Gubbi volcano in Ethiopia’s Afar region has erupted for the first time in almost 12,000 years, sending massive ash plumes soaring up to 14 kilometres into the atmosphere, according to the Toulouse Volcanic Ash Advisory Centre.
The eruption began on Sunday and lasted several hours. Hayli Gubbi, located around 800 kilometres northeast of Addis Ababa near the Eritrean border, sits within the geologically active Rift Valley, where two major tectonic plates meet. The volcano rises roughly 500 metres above the surrounding landscape.
Ash from the eruption drifted across the region, spreading over Yemen, Oman, India, and parts of Pakistan. Satellite imagery and social-media videos captured a towering column of white smoke billowing into the sky.
The Smithsonian Institution’s Global Volcanism Program notes that Hayli Gubbi has no recorded eruptions during the Holocene, the period dating back about 12,000 years to the end of the last Ice Age.
Volcanologist Simon Carn of Michigan Technological University also confirmed on Bluesky that the volcano had “no record of Holocene eruptions.”
Science & Technology
Cloudflare outage easing after millions of internet users affected

A global outage at web-infrastructure firm Cloudflare began to ease on Tuesday afternoon after preventing people from accessing major internet platforms, including X and ChatGPT.
Cloudflare, whose network handles around a fifth of web traffic, said it started to investigate the internal service degradation around 6:40 a.m. ET. It has deployed a fix but some customers might still be impacted as it recovers service.
The incident marked the latest hit to major online services. An outage of Amazon’s cloud service last month caused global turmoil as thousands of popular websites and apps, including Snapchat, were inaccessible due to the disruption.
Cloudflare – whose shares were down about 5% in premarket trading – runs one of the world’s largest networks that helps websites and apps load faster and stay online by protecting them from traffic surges and cyberattacks.
The latest outage prevented users from accessing platforms such as Canva, X, and ChatGPT, prompting users to log outage reports with Downdetector.
Downdetector tracks outages by collating status reports from a number of sources. “We saw a spike in unusual traffic to one of Cloudflare’s services beginning at 11:20 UTC. That caused some traffic passing through Cloudflare’s network to experience errors,” the company said in an emailed statement.
“We are all hands on deck to make sure all traffic is served without errors.”
X and ChatGPT-creator OpenAI did not immediately respond to requests for comment. – REUTERS
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoGermany speeds up admission of Afghans from Pakistan
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoIPL 2026 Auction set for Abu Dhabi with $28.6 million purse at stake
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoAfghan economy posts second year of growth despite deep structural challenges
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoAfghanistan to establish independent oil and gas authority
-

 Sport5 days ago
Sport5 days agoATN to broadcast ‘The Best FIFA Football Awards 2025’
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoUS intelligence chief warns of ‘direct threat’ from suspected terrorists inside the country
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoIEA supreme leader stresses enforcement of Sharia law and sincere public service
-

 International Sports4 days ago
International Sports4 days agoILT20: Desert Vipers qualify for playoffs with five-wicket win over Dubai Capitals