Health
Afghans with TB ‘struggling’ to get accessible treatment: MSF

Afghanistan’s broken economy and dysfunctional health care system has left thousands of patients in a vulnerable situation across the country, especially people with tuberculosis (TB).
According to Doctors Without Borders/Médecins Sans Frontières (MSF) there is a critical shortage of advanced medical treatment available for TB patients, coupled with a widespread lack of knowledge about the disease.
One such example is Jawahira who was referred to MSF’s tuberculosis (TB) hospital in Kandahar earlier this year from a clinic in Daikundi, in central Afghanistan. “I used to visit private clinics, but instead of giving me TB medication, they usually just prescribed painkillers,” she said.
MSF’s 24-bed TB hospital in Kandahar is the only medical facility providing advanced TB care in southern Afghanistan. Many of the patients come from the nearby provinces of Helmand, Uruzgan, Nimroz and Zabul, but others travel from more than 500 kms away, from Farah, Daikundi, Badghis, Ghazni, and Paktika provinces.
“Our catchment area is so big, it is impossible to know exactly how many people are in it,” said MSF medical advisor Allieu Tommy. “Many travel from afar, and we support them by paying for transport costs, housing expenses, and food to alleviate some of the economic burden.” Without such incentives, most patients could not afford to come for treatment.
The cost of searching for treatment also took its toll on Jawahira. “My home is far away in Uruzgan, so when we went to see a doctor, I had to spend 6,000 Afghani ($67) for the car fare and then 13,000 ($146) for the drugs they gave me.”
The amount Jawahira spent on each visit to the doctor is about one-third of the average monthly income in Afghanistan. According to the World Bank, an estimated 60 percent of the country’s population is unemployed and has no income at all, exacerbated by sanctions and other financial measures against the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan (IEA).
People often struggle to afford even basic food items, let alone travel expenses and medical fees for hospital visits. Meanwhile, the public health care system is under-resourced, under-staffed, and under-funded, MSF said.
The father of another patient at the Kandahar hospital, Hamdullah, said: “Our daughter Bibi is nine years old and has been sick since childhood, but we did not know of her illness — we had never heard the name TB before.”
MSF teams carry out regular health promotion activities in local communities in Kandahar to spread awareness about TB. They also provide information to patients and caretakers at the hospital in Kandahar.
“When a person arrives for the first time and learns that they have TB, we talk to them about what it is, how it’s transmitted, how to be careful around family members, and how long the treatment will take,” explained MSF nurse Taiba Azizi.
Providing this information is simple but effective. “Now I understand the symptoms and people back home know it is a dangerous disease,” said Hamdullah. “If somebody had seen her [Bibi] earlier, they would have said she would not recover. But now, we know she can get past this. She has already started to eat and walk. We hope she is getting better.”
MSF also tests a patient’s family for TB, as the disease is highly transmissible, particularly when people live close together.
MSF stated that some patients have a form of the disease that is resistant to conventional TB drugs and requires treatment that lasts nine to 12 months. This can be especially difficult to cope with during a hospital stay, far from friends and relatives. As a result, many patients stop their treatment early.
But next year, a six-month short course regimen will be rolled out that should make it easier for people to finish their treatment.
MSF has already set up a diagnose and treatment program that combines specialist inpatient care with supervised home-based treatment to help patients better cope with the regimens.
“What we offer is a system whereby a person spends the first 30 days in our facility under careful observation and, if they do not experience major adverse side effects from the drugs taken, they are discharged for homecare,” said Azizi.
“Our staff then do weekly follow-ups over the phone, so patients only need to come back to the hospital once a month to renew their medications and have an in-person consultation.”
Women and children are most vulnerable to TB
Over 70 percent of patients in MSF’s Kandahar TB hospital are women and children. “Women and children stay at home in dusty, poorly ventilated rooms for longer periods of time than men,” said Tommy.
“If a woman gets infected, the children are likely to catch the disease as well. Other cultural factors play a role too. Women whisper or speak in very low tones to one another, especially if men are in the room. Respiratory tract infections are then easily transmissible due to their proximity.”
An additional challenge for female patients is that they are generally required to be accompanied by a male family member to the hospital, and this coupled with the economic barriers can significantly reduce their access to health care.
It is estimated that TB and its resistant forms kill more than 13,000 people in Afghanistan every year.
Access to proper care remains a major challenge for patients in the southern part of the country, mainly due to insufficient medical infrastructure, length of treatment, and financial obstacles. While MSF’s TB hospital in Kandahar provides free quality treatment for many, the people of Afghanistan need a more robust and sustainable health care system to meet their many urgent needs, MSF stated.
Health
Afghan delegation heads to Turkey for medicine talks

Naemullah Ayoubi, Director General of Drug and Health Products Regulation at Afghanistan’s Ministry of Public Health, has departed for Turkey on an official visit accompanied by a technical delegation.
The Ministry of Public Health said the delegation will hold meetings with officials from Turkey’s pharmaceutical regulatory authority and discuss a number of key issues related to the regulation of medicines and health products.
The delegation is also scheduled to visit several pharmaceutical manufacturing factories in Turkey.
According to the ministry, the visit aims to strengthen coordination between the two countries in the production and import of medicines, in order to ensure the availability of high-quality and affordable pharmaceuticals for people in Afghanistan in both the short and long term.
Health
Afghanistan opens first national cancer diagnosis and treatment hospital
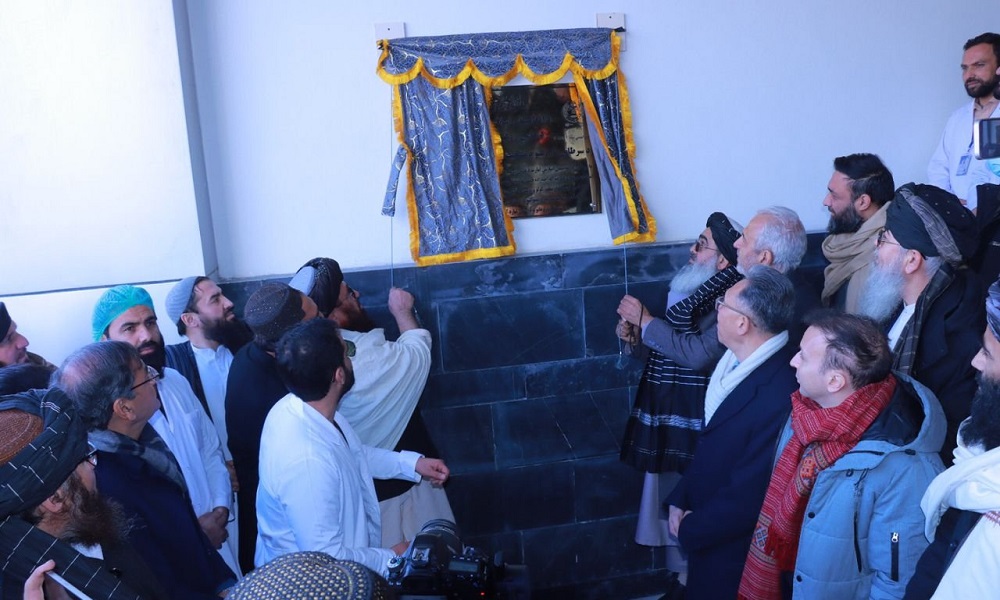

The Ministry of Public Health announced on Thursday that Afghanistan has inaugurated its first national hospital dedicated to the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, marking a major step forward in the country’s healthcare services.
The facility, named the National Cancer Diagnostic and Therapeutic Hospital, has officially begun operations and will provide specialized care for cancer patients across the country.
Speaking at the inauguration ceremony, Public Health Minister Noor Jalal Jalali said the 200-bed hospital aims to offer hope and improved treatment options for patients suffering from cancer.
“Fortunately, we are jointly opening a 200-bed hospital for cancer patients, and we hope that this hospital will become a source of hope and healing for those in need,” Jalali said.
The minister added that specialized training programs will soon be launched at the hospital to educate and train domestic medical specialists. He noted that reforms have already been implemented to improve facilities and ensure better healthcare services.
Jalali also emphasized international cooperation in the project, saying that radiotherapy services will be introduced at the hospital with support from India. According to the ministry, India has so far provided $1 million in assistance, including 10 tons of medicines and medical equipment, to support cancer treatment in Afghanistan.
The opening of the hospital is expected to reduce the need for Afghan patients to seek costly cancer treatment abroad and improve access to specialized care inside the country.
Health
Pakistan becomes latest Asian country to introduce checks for deadly Nipah virus
Authorities in Pakistan have ordered enhanced screening of people entering the country for signs of infections of the deadly Nipah virus after India confirmed two cases, adding to the number of Asian countries stepping up controls.
Thailand, Singapore, Hong Kong, Malaysia, Indonesia and Vietnam have also tightened screening at airports, Reuters reported.
The Nipah virus can cause fever and brain inflammation and has a high mortality rate. There is also no vaccine. But transmission from person to person is not easy and typically requires prolonged contact with an infected individual.
“It has become imperative to strengthen preventative and surveillance measures at Pakistan’s borders,” the Border Health Services department said in a statement.
“All travelers shall undergo thermal screening and clinical assessment at the Point of Entry,” which includes seaports, land borders and airports, the department added.
The agency said travellers would need to provide transit history for the preceding 21-day period to check whether they had been through “Nipah-affected or high-risk regions”.
There are no direct flights between Pakistan and India and travel between the two countries is extremely limited, particularly since their worst fighting in decades in May last year.
In Hanoi, the Vietnamese capital’s health department on Wednesday also ordered the screening of incoming passengers at Noi Bai airport, particularly those arriving from India and the eastern state of West Bengal, where the two health workers were confirmed to have the virus in late December.
Passengers will be checked with body temperature scanners to detect suspected cases. “This allows for timely isolation, epidemiological investigation,” the department said in a statement.
That follows measures by authorities in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam’s largest city, who said they had tightened health controls at international border crossings.
India’s health ministry said this week that authorities have identified and traced 196 contacts linked to the two cases with none showing symptoms and all testing negative for the virus.
Nipah is a rare viral infection that spreads largely from infected animals, mainly fruit bats, to humans. It can be asymptomatic but it is often very dangerous, with a case fatality rate of 40% to 75%, depending on the local healthcare system’s capacity for detection and management, according to the World Health Organization.
The virus was first identified just over 25 years ago during an outbreak among pig farmers in Malaysia and Singapore, although scientists believe it has circulated in flying foxes, or fruit bats, for thousands of years.
The WHO classifies Nipah as a priority pathogen. India regularly reports sporadic infections, particularly in the southern state of Kerala, regarded as one of the world’s highest-risk regions for Nipah.
As of December 2025, there have been 750 confirmed Nipah infections globally, with 415 deaths, according to the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations, which is funding a vaccine trial to help stop Nipah.
-

 Sport5 days ago
Sport5 days agoHosts and heavyweights advance as AFC Futsal Asian Cup reaches semifinals
-

 Latest News4 days ago
Latest News4 days agoTerrorist threat in Afghanistan must be taken seriously, China tells UNSC
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoUzbekistan, Pakistan advance Trans-Afghan railway project
-

 Sport5 days ago
Sport5 days agoWinter Olympics finally underway, ATN to broadcast exclusively across Afghanistan
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoAfghanistan beat West Indies in final T20 WC warm-up match
-

 Latest News1 day ago
Latest News1 day agoAfghanistan to grant one- to ten-year residency to foreign investors
-

 Sport3 days ago
Sport3 days agoIndonesia shock Japan to reach historic AFC Futsal Asian Cup final
-

 Regional5 days ago
Regional5 days agoPakistan sends helicopters, drones to end desert standoff; 58 dead
























