World
US strikes may have set back Iran nuclear program only months, sources say
A U.S. official, speaking on condition of anonymity, said the U.S. did not yet know the true extent of the damage.
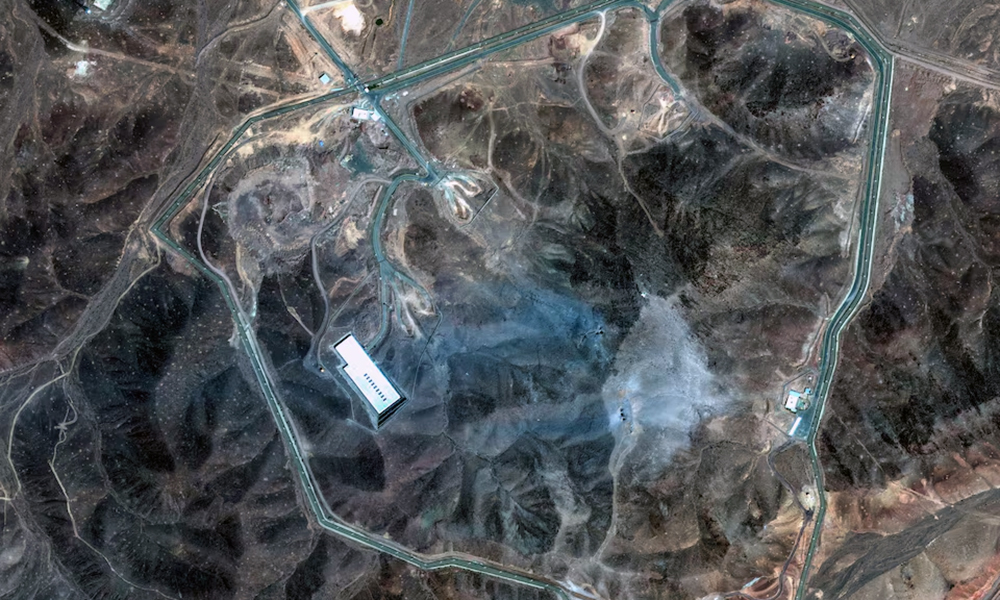

A preliminary U.S. intelligence assessment has determined that U.S. strikes over the weekend on Iranian nuclear facilities have set back Tehran’s program by only a matter of months, three sources with knowledge of the matter told Reuters.
The initial report was prepared by the Defense Intelligence Agency, the Pentagon’s main intelligence arm and one of 18 U.S. intelligence agencies, said two of the sources, who requested anonymity to discuss classified matters.
The assessment found that Iran could restart its nuclear program in a matter of months, according to the three sources, one of whom said it estimated the earliest restart could be in one to two months.
The classified assessment is at odds with the statements of President Donald Trump and high-ranking U.S. officials – including Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth. They have said the weekend strikes, which used a combination of bunker-busting bombs and more conventional weapons, essentially eliminated Iran’s nuclear program.
Trump’s administration on Tuesday told the U.N Security Council that its weekend strikes had “degraded” Iran’s nuclear program, short of Trump’s earlier assertion that the facilities had been “obliterated.”
Asked for comment, the White House pointed to a statement by spokesperson Karoline Leavitt to CNN, which first reported the assessment, that the “alleged” conclusion was “flat-out wrong.”
“Everyone knows what happens when you drop fourteen 30,000 pound bombs perfectly on their targets: total obliteration,” she said.
A U.S. official who read the assessment noted that it contained a number of caveats and “ifs” and said a more refined report was expected in the coming days and weeks.
Analysts said that, if the assessment was based on satellite imagery, the extent of damage to the deeply buried Fordow uranium enrichment facility would not necessarily be revealed.
Trump has said the attacks were necessary to prevent Iran from developing a nuclear weapon. Iran denies it is seeking such a weapon and says its nuclear program is for peaceful purposes.
Assessing the damage at the Fordow, Isfahan and Natanz nuclear sites is expected to be a difficult task, and the DIA is not the only agency tasked with the job. One source said the assessment was not universally accepted and had generated significant disagreement.
A U.S. official, speaking on condition of anonymity, said the U.S. did not yet know the true extent of the damage.
Still, the initial assessment indicated the strikes may not have been nearly as successful as the Trump administration has claimed.
The sources said that the report found that the U.S. attack had caved in facility entrances and destroyed or damaged infrastructure. However, one added, the strike did not collapse underground buildings.
Restarting operations would basically depend on “how long it takes them to dig out and build or repair” power and water supply facilities, said the second source.
The Washington Post, citing a person familiar the report, said some centrifuges for enriching uranium were intact.
The Pentagon disputed the notion that the damage was insignificant, though it did not dispute that the DIA assessment exists.
“Based on everything we have seen — and I’ve seen it all — our bombing campaign obliterated Iran’s ability to create nuclear weapons,” Hegseth said in a statement to Reuters.
“Our massive bombs hit exactly the right spot at each target—and worked perfectly. The impact of those bombs is buried under a mountain of rubble in Iran; so anyone who says the bombs were not devastating is just trying to undermine the President and the successful mission.”
One source, however, said Iran’s enriched uranium stocks had not been eliminated.
David Albright, a former U.N. nuclear inspector, said that based on post-strike commercial satellite imagery, he believed the U.S. attack effectively destroyed Iran’s uranium enrichment program for now, but failed to eliminate the longer-term threat.
“Iran retains an ability to break out and produce weapon-grade uranium,” said Albright, the head of the Institute for Science and International Security, in a post on X.
He noted that Iran’s stock of near-weapons grade highly enriched uranium – enough for about nine warheads – is unaccounted for as are advanced centrifuges for a new enrichment facility that Iran this month told the IAEA it was preparing.
Initial military assessments can change as more information comes to light and it is not uncommon for opinions to vary across different U.S. intelligence agencies.
Democrats have previously said Trump’s claims that the weekend strikes eliminated or seriously set back Iran’s nuclear program were not yet backed by evidence.
“There’s zero evidence that I’ve seen that the nuclear program was completely and totally obliterated as Donald Trump has claimed,” House of Representatives Democratic Leader Hakeem Jeffries said on Monday.
Classified briefings on the matter for members of the House of Representatives and Senate were canceled on Tuesday.
World
Top US, Israeli generals meet at Pentagon amid soaring Iran tensions
The officials did not offer details about the closed-door discussions between U.S. General Dan Caine, the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, and Eyal Zamir, the Israeli armed forces chief of staff.

The top U.S. and Israeli generals held talks at the Pentagon on Friday amid soaring tensions with Iran, two U.S. officials told Reuters on Sunday, speaking on condition of anonymity, Reuters reported.
The officials did not offer details about the closed-door discussions between U.S. General Dan Caine, the chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, and Eyal Zamir, the Israeli armed forces chief of staff. The meeting has not been previously reported.
The United States has ramped up its naval presence and hiked its air defences in the Middle East after President Donald Trump repeatedly threatened Iran, trying to pressure it to the negotiating table. Iran’s leadership warned on Sunday of a regional conflict if the U.S. were to attack it, read the report.
Israeli Defence Minister Israel Katz on Sunday met with Zamir after his talks in Washington, Katz’s office said, to review the situation in the region and the Israeli military’s “operational readiness for any possible scenario.”
World
Israeli attacks kill 31 Palestinians in Gaza, including children
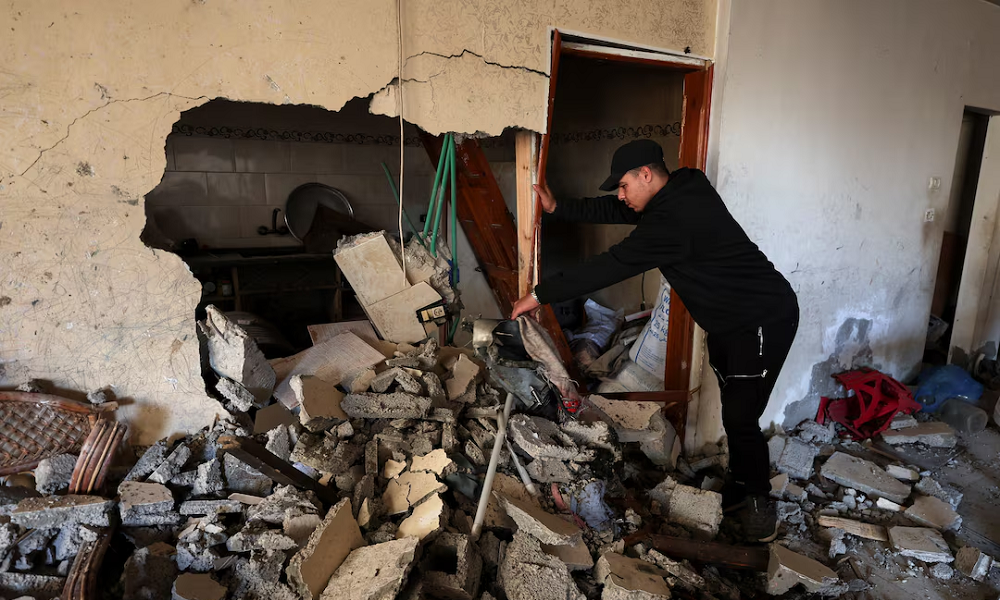

At least 31 Palestinians, including six children, were killed in Israeli attacks on Gaza City and Khan Younis since early Saturday, according to medical sources cited by Al Jazeera.
The strikes came a day before Israel is scheduled to reopen the Rafah crossing between Gaza and Egypt on Sunday, marking the first reopening of the border crossing since May 2024.
Gaza’s Government Media Office said that more than 500 Palestinians have been killed by Israeli forces since a United States-brokered ceasefire came into effect on October 10.
According to local health authorities, Israel’s military campaign in Gaza has killed at least 71,769 Palestinians and wounded 171,483 others since it began in October 2023. In Israel, at least 1,139 people were killed during the Hamas-led attacks on October 7, 2023, with approximately 250 people taken captive.
World
Guterres warns of UN’s ‘imminent financial collapse’
In his letter, Guterres said “decisions not to honour assessed contributions that finance a significant share of the approved regular budget have now been formally announced.”
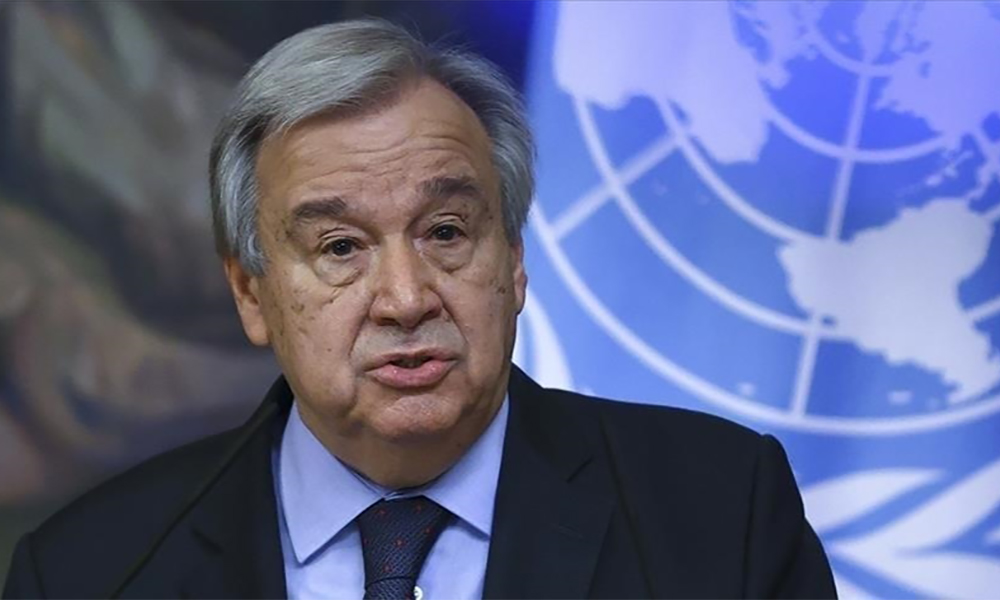

The U.N. chief has told member states the organisation is at risk of “imminent financial collapse,” citing unpaid fees and a budget rule that forces the global body to return unspent money, a letter seen by Reuters on Friday showed.
U.N. Secretary-General Antonio Guterres has repeatedly spoken about the organisation’s worsening liquidity crisis but this is his starkest warning yet, and it comes as its main contributor the U.S. is retreating from multilateralism on numerous fronts.
“The crisis is deepening, threatening programme delivery and risking financial collapse. And the situation will deteriorate further in the near future,” Guterres wrote in a letter to ambassadors dated January 28.
The U.S. has slashed voluntary funding to U.N. agencies and refused to make mandatory payments to its regular and peacekeeping budgets.
U.S. President Donald Trump has described the U.N. as having “great potential” but said it is not fulfilling that, and he has launched a Board of Peace which some fear could undermine the older international body.
Founded in 1945, the U.N. has 193 member states and works to maintain international peace and security, promote human rights, foster social and economic development, and coordinate humanitarian aid.
In his letter, Guterres said “decisions not to honour assessed contributions that finance a significant share of the approved regular budget have now been formally announced.”
He did not say which state or states he was referring to, and a U.N. spokesperson was not immediately available for comment.
Under U.N. rules, contributions depend on the size of the economy of each member state. The U.S. accounts for 22% of the core budget followed by China with 20%.
But by the end of 2025 there was a record $1.57 billion in outstanding dues, Guterres said, without naming the nations that owed them.
“Either all Member States honour their obligations to pay in full and on time – or Member States must fundamentally overhaul our financial rules to prevent an imminent financial collapse,” he said.
U.N. officials say the U.S. currently owes $2.19 billion to the regular U.N. budget, another $1.88 billion for active peace-keeping missions and $528 million for past peace-keeping missions.
The U.S. State Department did not immediately respond to a request for comment on the Guterres letter.
Guterres launched a reform task force last year, known as UN80, which seeks to cut costs and improve efficiency. To that end, states agreed to cut the 2026 budget by around 7% to $3.45 billion.
Still, Guterres warned in the letter that the organisation could run out of cash by July.
One of the problems is a rule now seen as antiquated whereby the global body has to credit back hundreds of millions of dollars in unspent dues to states each year.
“In other words, we are trapped in a Kafkaesque cycle expected to give back cash that does not exist,” said Guterres, referring to author Franz Kafka who wrote about oppressive bureaucratic processes.
-

 Sport5 days ago
Sport5 days agoAfghanistan shine on Day Two of AFC Futsal Asian Cup Indonesia 2026
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoAfghanistan eye second straight win ahead of Malaysia clash at AFC Futsal Asian Cup
-

 Sport2 days ago
Sport2 days agoAFC Futsal Asian Cup: Afghanistan to face Iran in crucial Group D clash
-

 Sport3 days ago
Sport3 days agoAfghanistan dominates Malaysia 7–0 in AFC Futsal Asian Cup
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoAustralia announces $50 million in new humanitarian aid for Afghanistan
-

 Sport2 days ago
Sport2 days agoT20 World Cup 2026: Afghanistan national cricket team arrives in India
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoPakistan, China plan to extend CPEC to Afghanistan, revive trilateral framework
-
 Health5 days ago
Health5 days agoPakistan becomes latest Asian country to introduce checks for deadly Nipah virus
























