Business
World Bank warns global economy could tip into recession in 2023

The World Bank slashed its 2023 growth forecasts on Tuesday to levels teetering on the brink of recession for many countries as the impact of central bank rate hikes intensifies, Russia’s war in Ukraine continues, and the world’s major economic engines sputter.
The development lender said it expected global GDP growth of 1.7% in 2023, the slowest pace outside the 2009 and 2020 recessions since 1993. In its previous Global Economic Prospects report in June 2022, the bank had forecast 2023 global growth at 3.0%, Reuters reported.
It forecast global growth in 2024 to pick up to 2.7% — below the 2.9% estimate for 2022 — and said average growth for the 2020-2024 period would be under 2% — the slowest five-year pace since 1960.
The bank said major slowdowns in advanced economies, including sharp cuts to its forecast to 0.5% for both the United States and the euro zone, could foreshadow a new global recession less than three years after the last one.
“Given fragile economic conditions, any new adverse development — such as higher-than-expected inflation, abrupt rises in interest rates to contain it, a resurgence of the COVID-19 pandemic or escalating geopolitical tensions — could push the global economy into recession,” the bank said in a statement accompanying the report.
The bleak outlook will be especially hard on emerging market and developing economies, the World Bank said, as they struggle with heavy debt burdens, weak currencies and income growth, and slowing business investment that is now forecast at a 3.5% annual growth rate over the next two years — less than half the pace of the past two decades.
“Weakness in growth and business investment will compound the already devastating reversals in education, health, poverty and infrastructure and the increasing demands from climate change,” World Bank President David Malpass said in a statement.
China’s growth in 2022 slumped to 2.7%, its second slowest pace since the mid-1970s after 2020, as zero-COVID restrictions, property market turmoil and drought hit consumption, production and investment, the World Bank report said. It predicted a rebound to 4.3% for 2023, but that is 0.9 percentage-point below the June forecast due to the severity of COVID disruptions and weakening external demand.
The World Bank noted that some inflationary pressures started to abate as 2022 drew to a close, with lower energy and commodity prices, but warned that risks of new supply disruptions were high, and elevated core inflation may persist. This could cause central banks to respond by raising policy rates by more than currently expected, worsening the global slowdown, it added.
The bank called for increased support from the international community to help low-income countries deal with food and energy shocks, people displaced by conflicts, and a growing risk of debt crises. It said new concessional financing and grants are needed along with the leveraging of private capital and domestic resources to help boost investment in climate adaptation, human capital and health, the report said.
The report comes as the World Bank’s board this week is expected to consider a new “evolution road map” for the institution to vastly expand its lending capacity to address climate change and other global crises. The plan will guide negotiations with shareholders, led by the United States, for the biggest revamp in the bank’s business model since its creation at the end of World War Two.
Business
Uzbekistan approves feasibility study agreement for Trans-Afghan Railway
The agreement builds on a tripartite document signed on July 17, 2025, which outlined cooperation on preparing a feasibility study for the Termez–Kharlachi railway corridor.
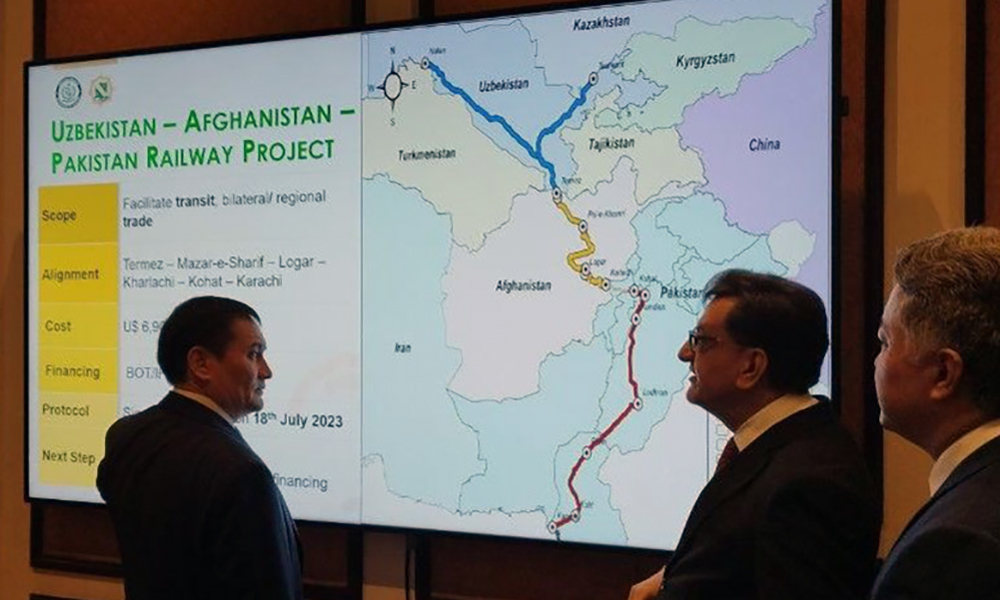
Uzbekistan has ratified an international agreement to prepare a feasibility study for the Naybabad–Kharlachi section of the Trans-Afghan Railway, formalizing its participation in the project.
President Shavkat Mirziyoyev signed a decree on February 4 approving the agreement.
The framework agreement involves the transport ministries of Uzbekistan, Afghanistan and Pakistan and provides for joint work on a feasibility study for the proposed railway line between Naybabad and Kharlachi. The section forms part of the wider Trans-Afghan Railway project aimed at strengthening transport links between Central and South Asia.
Under the decree, Uzbekistan’s Ministry of Transport has been designated as the competent authority responsible for implementing the agreement. The Ministry of Foreign Affairs has been tasked with notifying Kabul and Islamabad that Uzbekistan has completed the internal procedures required for the agreement to enter into force.
The agreement builds on a tripartite document signed on July 17, 2025, which outlined cooperation on preparing a feasibility study for the Termez–Kharlachi railway corridor.
The planned route is expected to run through Termez, Naybabad, Maidanshahr, Logar and Kharlachi, providing a transit corridor through Afghanistan.
The feasibility study will be commissioned by the Tripartite Project Office for the Development Strategy of International Transport Corridors under Uzbekistan Railways.
Established in Tashkent in May 2023, the office also operates branches in Kabul and Islamabad to coordinate the project.
First proposed in 2018, the Trans-Afghan Railway was initially projected to carry up to 20 million tons of cargo annually at a cost of about $5 billion. Cost estimates have since been revised.
In July 2022, Uzbekistan Railways cited an estimate of $4.6 billion with a construction period of up to five years, while Pakistan’s Ministry of Railways put the cost at $8.2 billion in December 2024.
More recent assessments have placed the overall cost at around $7 billion, with a public-private partnership under a Build-Operate-Transfer model among the options under consideration.
Business
Afghanistan seeks expanded ties with Russia in energy, mining and infrastructure
TASS reported that Kabul is also prepared to cooperate with Moscow in the extraction of mineral resources.

Afghanistan has expressed strong interest in broadening trade and economic cooperation with Russia, with a particular focus on energy, mining and infrastructure projects, according to Russia’s TASS news agency.
In an interview with TASS, Afghanistan’s Ambassador to Moscow, Gul Hassan, said Kabul is keen to import oil and gas from Russia as part of efforts to deepen bilateral economic ties.
He noted that trade relations between the two countries are progressing and that, if key obstacles—especially banking restrictions—are addressed, Afghanistan could also import medicines, industrial goods, grain, vegetable oils and other commodities from Russia.
In return, the ambassador said Afghanistan is ready to export fresh and dried fruits, vegetables, medicinal plants, carpets and mineral resources to the Russian market, adding that expanding export-import operations could significantly increase bilateral trade volumes.
He also revealed plans to open an exhibition of Afghan products in Moscow, which he said would help boost trade turnover.
TASS reported that Kabul is also prepared to cooperate with Moscow in the extraction of mineral resources.
Hassan described the economy as a central pillar of Afghanistan’s foreign policy, emphasizing the government’s goal of positioning the country as a key link in regional economic integration and attracting foreign investment.
He noted that Russian companies have long shown interest in Afghanistan’s industrial, mining and infrastructure sectors.
The ambassador further told TASS that Russian firms are already in talks with relevant Afghan authorities on the construction of small hydroelectric power plants.
Representatives of several Russian companies have reportedly visited Afghanistan and held meetings with officials and technical experts.
According to Hassan, practical steps toward cooperation in the energy and power generation sectors are expected in the near future, pointing to a potential new phase in Afghan-Russian economic relations.
Business
Pakistan, China plan to extend CPEC to Afghanistan, revive trilateral framework
The proposed CPEC expansion into Afghanistan is seen as a move to enhance regional economic integration amid shifting geopolitical dynamics.

Pakistan and China are moving forward with plans to extend the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) into Afghanistan, a strategic step aimed at bolstering regional connectivity and economic cooperation. The expansion, along with the revival of the Pakistan-China-Afghanistan trilateral framework, was discussed in a recent briefing to the Pakistani Senate Standing Committee on Foreign Affairs.
According to Pakistan Today, officials from Pakistan’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs outlined the details during a session in Islamabad, where they reviewed key aspects of Pakistan’s foreign relations, regional developments, and economic diplomacy.
Officials emphasized that Pakistan’s relationship with China remains strong, underscoring the “all-weather” strategic partnership between the two nations. Strengthening ties with Beijing, they stated, continues to be a cornerstone of Pakistan’s foreign policy. This includes unwavering support for China’s position on regional and international issues, particularly the One-China policy and matters related to territorial integrity.
The briefing also touched upon China’s consistent backing of Pakistan in various areas, including sovereignty, economic stability, counter-terrorism, and support for Pakistan’s exit from the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) grey list.
The Kashmir issue was also addressed, with officials noting that China considers it an unresolved matter and advocates for a peaceful resolution in line with UN Security Council resolutions.
The proposed CPEC expansion into Afghanistan is seen as a move to enhance regional economic integration amid shifting geopolitical dynamics. Officials stated that reviving the trilateral framework is part of broader efforts to foster greater cooperation and connectivity in the region, with an eye on long-term stability and prosperity.
The move also reflects both countries’ desire to further integrate Afghanistan into the regional economic landscape, a key element in fostering peace and development.
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoAfghanistan to grant one- to ten-year residency to foreign investors
-

 Sport4 days ago
Sport4 days agoIndonesia shock Japan to reach historic AFC Futsal Asian Cup final
-

 Sport3 days ago
Sport3 days agoIran clinch AFC Futsal Asian Cup 2026 in penalty shootout thriller
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoAfghanistan says Pakistan is shifting blame for its own security failures
-

 International Sports2 days ago
International Sports2 days agoWinter Olympics gain momentum as medal table takes shape
-

 Latest News5 days ago
Latest News5 days agoAfghanistan facing deepening hunger crisis after US Aid Cuts: NYT reports
-

 World5 days ago
World5 days agoUS, Ukraine, Russia delegations agree to exchange 314 prisoners, says Witkoff
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoTraffic police receive new cars

























